25 Vulnerabilities Found in Cloud Password Managers

Researchers from ETH Zurich discovered 25 serious vulnerabilities in Bitwarden, LastPass, and Dashlane cloud password managers. These flaws let malicious servers bypass zero-knowledge encryption claims to access, modify, or recover user vaults. The three services protect over 60 million users worldwide.
The attacks work under a malicious server model where cloud infrastructure deviates from protocols. Despite vendor claims of end-to-end encryption, servers can compromise confidentiality and integrity. ETH disclosed findings responsibly to all three vendors.
Bitwarden faced 12 attacks, LastPass 7, and Dashlane 6. Issues span key escrow flaws, item encryption weaknesses, sharing exploits, and legacy compatibility bugs. Many require just one user interaction like a login or sync.
ETH Zurich Research Details
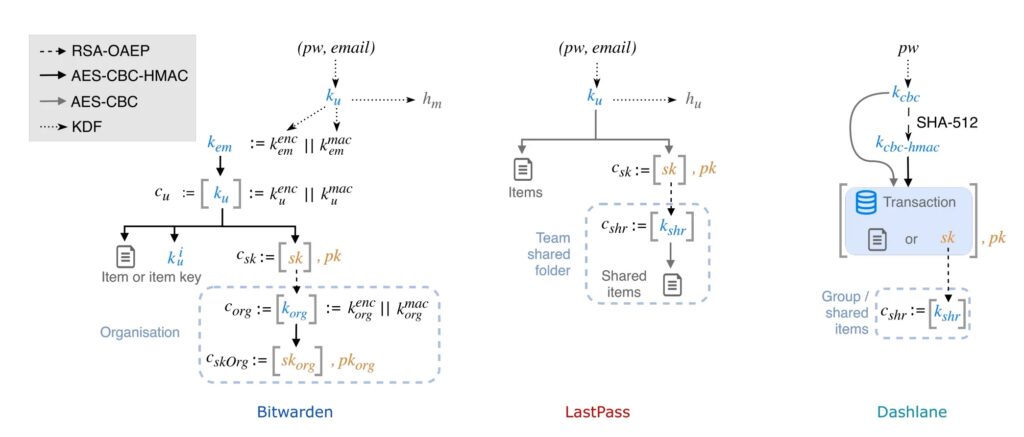
ETH researchers tested client-server interactions against fully compromised servers. They found zero-knowledge protections fail across recovery, sharing, and encryption layers. Full technical paper available through university channels.
Vendors received coordinated disclosure. Bitwarden got notice January 27, 2025. LastPass on June 4, 2025. Dashlane on August 29, 2025. All followed 90-day remediation windows. ETH announcement
Attack Categories Breakdown
Key Escrow Attacks: Recovery and SSO flaws enable unauthenticated key substitution. Attackers rotate or convert keys during organization joins or dialogs.
Item-Level Encryption Flaws: Missing authentication, key separation, and weak ciphers leak metadata, enable field swaps, and remove brute-force protections.
Sharing Exploits: Public keys lack authentication. Attackers inject organization members or overwrite shared vault keys on join.
Backwards Compatibility: Legacy AES-CBC support triggers downgrades. Protection mechanisms disable after syncs or logins.
Complete Vulnerability Table
| Attack Ref | Product | Root Cause | Impact | Client Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BW01 | Bitwarden | No Key Auth, Key Substitution | Full vault compromise | 1 join |
| BW02 | Bitwarden | Key Substitution | Full vault compromise | 1 rotation |
| BW03 | Bitwarden | No Key Auth, Key Substitution | Full vault compromise | 1 dialog |
| LP01 | LastPass | No Key Auth | Full vault compromise | 1 login |
| BW04 | Bitwarden | No Auth Enc | Read/modify metadata | – |
| BW05 | Bitwarden | No Key Separation | Field/item swapping | – |
| BW06 | Bitwarden | No Key Separation | Loss of confidentiality | 1 open |
| BW07 | Bitwarden | No Auth Enc | No brute-force protection | 1 login |
| LP02 | LastPass | No Auth Enc | Field/item swapping | – |
| LP03 | LastPass | No Key Separation | Loss of confidentiality | 1 open |
| LP04 | LastPass | No Auth Enc | No brute-force protection | 1 login |
| LP05 | LastPass | No Auth Enc | Loss of vault integrity | – |
| DL01 | Dashlane | No Key Separation | Loss of vault integrity | – |
| BW08 | Bitwarden | No Key Auth | Add users to orgs | 1 sync |
| BW09 | Bitwarden | No Key Auth, Key Substitution | Org compromise | 1 join |
| LP07 | LastPass | No Key Auth | Shared vault compromise | 1 join |
| DL02 | Dashlane | No Key Auth | Shared vault compromise | 1 join |
| BW10 | Bitwarden | No Auth Enc | Downgrade key hierarchy | – |
| BW11 | Bitwarden | CBC Support | Loss of confidentiality | 2 logins |
| BW12 | Bitwarden | CBC Support | Full vault compromise | 2 logins |
| DL03 | Dashlane | CBC Support | Loss of vault integrity | 104 syncs |
| DL04 | Dashlane | CBC Support | No brute-force protection | 104 syncs |
| DL05 | Dashlane | CBC Support | Loss of confidentiality | 105 syncs |
| DL06 | Dashlane | CBC Support | No brute-force protection | 104 syncs |
| LP06 | LastPass | No Auth Enc | Read/modify metadata | – |
Vendor Response Status
Bitwarden fixed multiple issues including minimum KDF iterations and CBC removal. LastPass addressed LP03 vault confidentiality. Dashlane released extension 6.2544.1 patching CBC flaws.
Self-hosted deployments remain at risk if servers compromise. Cloud users protected by vendor patches.
Technical Attack Examples
BW01 Malicious Auto-Enrollment: Unauthenticated organization public keys substitute victim keys during joins. Single interaction compromises entire vault.
BW06 Icon Decryption: Client requests decrypt unprotected icon URLs, leaking passwords indirectly through metadata.
BW07 KDF Downgrade: Attackers remove PBKDF2 iterations, enabling 300,000x faster brute-force attacks.
DL01 Transaction Replay: Shared keys across transactions violate integrity. Attackers replay modified transactions indefinitely.
Recommended Mitigations
Researchers propose four fixes for password manager protocols:
- Authenticated Encryption (AE): Protect all ciphertext with integrity checks
- Full Key Separation (KS): Isolate encryption keys per field/item
- Public Key Authentication (PKA): Validate all public keys before use
- Ciphertext Signing (SC): Sign vault contents end-to-end
Users should update all clients immediately. Enable per-item encryption where available. Monitor vendor security bulletins closely.
Impact Scale
| Vendor | Vulnerabilities | Market Share | Users Affected |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitwarden | 12 | High growth | 10M+ |
| LastPass | 7 | Enterprise | 30M+ |
| Dashlane | 6 | Premium | 20M+ |
| Total | 25 | Dominant | 60M+ |
FAQ
Bitwarden (12), LastPass (7), Dashlane (6).
Full vault access, modification, key recovery via malicious servers.
Yes. Bitwarden: KDF/CBC fixes. LastPass: LP03. Dashlane: v6.2544.1.
No. Server compromise still works despite client updates.
AE, KS, PKA, SC protocols per ETH researchers.
Many need 1 login/sync. Worst case: 105 syncs (DL05).
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more






User forum
0 messages