Socomec DIRIS M-70 Gateway: Six Critical DoS Vulnerabilities Exposed

Cisco Talos researchers discovered six high-severity denial-of-service vulnerabilities in Socomec DIRIS M-70 IIoT gateways. The flaws affect firmware version 1.6.9 and enable remote attackers to crash devices via specially crafted Modbus messages. No authentication required for exploitation.
The DIRIS M-70 monitors power quality in data centers, hospitals, and industrial facilities. It handles Modbus RTU/TCP, BACnet IP, and SNMP over RS485/Ethernet. CVSS v3.1 scores range from 7.5 across all six flaws tracked as CVE-2025-54848 through CVE-2025-55222.

Access content across the globe at the highest speed rate.
70% of our readers choose Private Internet Access
70% of our readers choose ExpressVPN

Browse the web from multiple devices with industry-standard security protocols.

Faster dedicated servers for specific actions (currently at summer discounts)
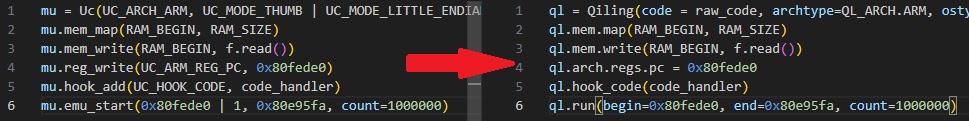
Researchers bypassed hardware debug protection using selective thread emulation. Full system emulation proved impractical due to STM32 microcontroller RDP Level 1 restrictions.
Traditional JTAG debugging failed against Code Readout Protection. Talos extracted unencrypted firmware for analysis. They emulated only the Modbus processing thread using Unicorn Engine, then applied AFL fuzzing.
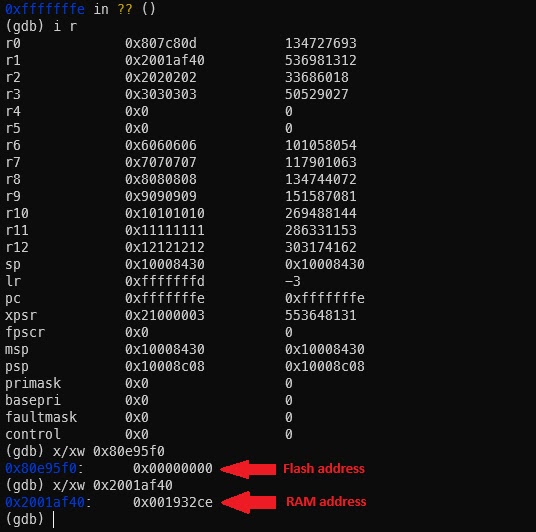
Over 700 Modbus message types made manual testing impossible. Fuzzing revealed buffer overflows and parsing errors triggering device reboots. Qiling framework later added coverage visualization.
Vulnerability Details Table
| CVE ID | CVSS Score | Attack Vector | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2025-54848 | 7.5 | Network | Device reboot |
| CVE-2025-54849 | 7.5 | Network | Modbus parser crash |
| CVE-2025-54850 | 7.5 | Network | Memory corruption |
| CVE-2025-54851 | 7.5 | Network | Stack overflow |
| CVE-2025-55221 | 7.5 | Network | Service disruption |
| CVE-2025-55222 | 7.5 | Network | Infinite loop |
All vulnerabilities require low complexity. No privileges or user interaction needed.
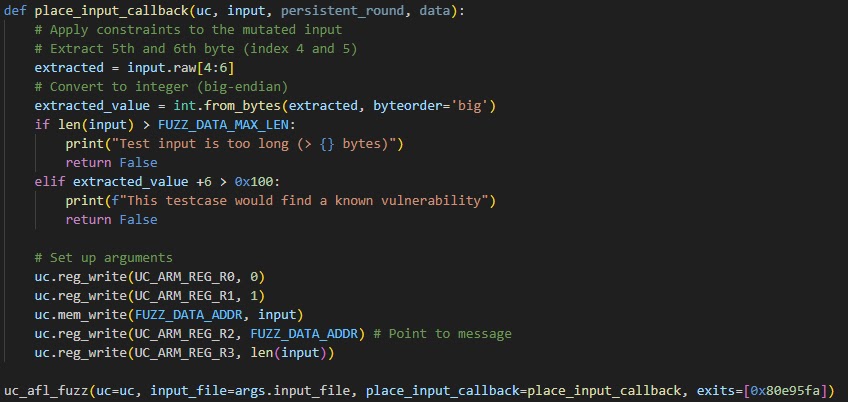
Emulation Methodology
Hardware limitations overcome:
- RDP Level 1 blocked JTAG flash reads
- Full ARM emulation too resource intensive
- 700+ Modbus handlers impractical manually
Selective thread approach:
1. Extract firmware → Identify Modbus thread
2. Unicorn Engine → Single thread execution
3. AFL fuzzing → Coverage-guided inputs
4. Qiling framework → Debug + visualization
This technique cut development time dramatically while achieving full vulnerability coverage.
Technical Discovery Process
Firmware analysis revealed Modbus thread isolation feasibility. Unicorn executed specific handlers without OS dependencies. AFL generated malformed Modbus TCP/RTU-over-TCP packets.
Crash analysis confirmed remote exploitability:
Modbus function code parsing flaws
Buffer boundary violations
Integer overflow conditions
State machine corruption
Each flaw independently crashes the gateway. Attackers chain multiple for persistent disruption.Affected Device Profile
DIRIS M-70 deployment:
- Power monitoring gateways
- RS485/Ethernet industrial comms
- Data centers, hospitals, factories
- Firmware 1.6.9 vulnerable
Attack surface:
Internet-facing management ports
Internal industrial networks
Remote SCADA access points
Impact Assessment
Operational consequences:
- Power monitoring blackout
- Energy management failure
- Equipment protection loss
- Safety system blind spots
Critical infrastructure risk:
Data center UPS monitoring offline
Hospital backup power tracking down
Manufacturing line power quality blind
CVSS Attack Vector: Network across all flaws.
Vendor Response Status
Socomec patches:
- Firmware 1.6.9 → 1.7+ resolves all issues
- Coordinated disclosure via Cisco policy
- Update immediately recommended
Detection rules:
SNORT signatures available: snort.org
Modbus anomaly detection
Traffic pattern analysis
Immediate Mitigation Steps
Network controls:
- Restrict Modbus TCP/RTU ports
- IP whitelist management access
- VLAN isolate IIoT devices
- OT network segmentation
Firmware management:
1. Backup current config
2. Download 1.7+ from Socomec
3. Verify update integrity
4. Apply during maintenance window
Detection Signatures
Network indicators:
Modbus malformed function codes
Excessive TCP RST from gateway
RS485 traffic spikes pre-crash
Port 502 anomalies
Device symptoms:
Intermittent reboots every 5-15min
Modbus timeout errors
Web interface unresponsive
SNMP polling failures
Research Innovation Value
Selective thread emulation proves superior for IIoT vulnerability discovery. Bypasses hardware protections while minimizing emulation complexity. AFL+Qiling combination accelerates fuzzing-debug cycles.
Key takeaways:
- Single-thread focus beats full emulation
- Firmware extraction essential
- Coverage-guided fuzzing scales to 700+ handlers
- RDP Level 1 no longer absolute barrier
Risk Prioritization
| Exposure | Priority | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Internet-facing | Critical | Firmware + firewall NOW |
| DMZ/SCADA | High | Firmware update + segment |
| Internal plant | Medium | Scheduled patching |
| Air-gapped | Low | Monitor vendor advisories |
FAQ
DIRIS M-70 IIoT power monitoring gateway firmware 1.6.9.
Six DoS flaws (CVE-2025-54848-55222), all CVSS 7.5 network attack vector.
Selective Modbus thread emulation with Unicorn+AFL+Qiling fuzzing.
Firmware 1.7+ from Socomec resolves all issues.
Data centers, healthcare, manufacturing critical infrastructure.
Remote unauthenticated Modbus TCP/RTU messages.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more






User forum
0 messages