How to Fix Windows 10 L2TP/IPSec Pre Shared Key Not Working (2025 Guide)
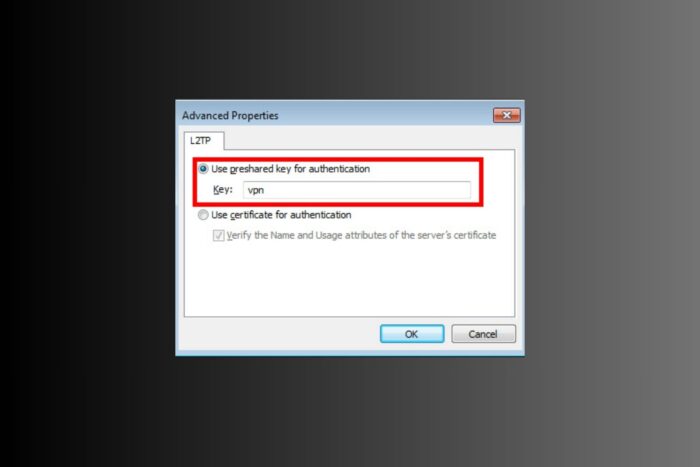
If your L2TP/IPsec VPN with a pre-shared key is not connecting on Windows 10 or 11, that can halt work fast. You might see the message “The L2TP connection attempt failed because the security layer encountered a processing error.”
This guide shows what is going on and how to fix it. Work through the fixes in order. After that, check the common reasons so you can prevent it from happening again. You can also check the Windows 11 L2TP/IPsec troubleshooting guide for comparison if you use multiple systems.

Access content across the globe at the highest speed rate.
70% of our readers choose Private Internet Access
70% of our readers choose ExpressVPN

Browse the web from multiple devices with industry-standard security protocols.

Faster dedicated servers for specific actions (currently at summer discounts)
Step-by-Step Fixes for L2TP/IPsec VPN Not Working on Windows 10
Table of contents
- Step-by-Step Fixes for L2TP/IPsec VPN Not Working on Windows 10
- 1. Check Your VPN Settings
- 2. Start Required Windows Services
- 3. Allow VPN Ports and Protocols
- 4. Enable NAT Traversal for VPN Connections
- 5. Reinstall WAN Miniport Adapters
- 6. Turn Off IPv6 Temporarily
- 7. Pause Antivirus or Firewall Protection
- 8. Check VPN Server Configuration
- 9. Remove Problematic Windows Updates
- 10. Fix VPN IP Conflicts
- 11. Reset Network Settings in Windows 10
- 12. Update Network Drivers
- 13. Flush DNS and Reset Winsock
- 14. Check the Event Viewer for VPN Errors
- 15. Create a New VPN Profile
- 16. Change DNS Settings
- 17. Update Router Firmware
- 18. Test with a Different Network
- Common Reasons Why L2TP/IPsec VPN Stops Working
- Quick Reference: L2TP/IPsec VPN Error Codes and Fixes
- FAQs About L2TP/IPsec VPN on Windows 10
- Final Verdict: Fixing L2TP/IPsec VPN Problems on Windows 10
Try these one by one. Test the connection after each step.
1. Check Your VPN Settings
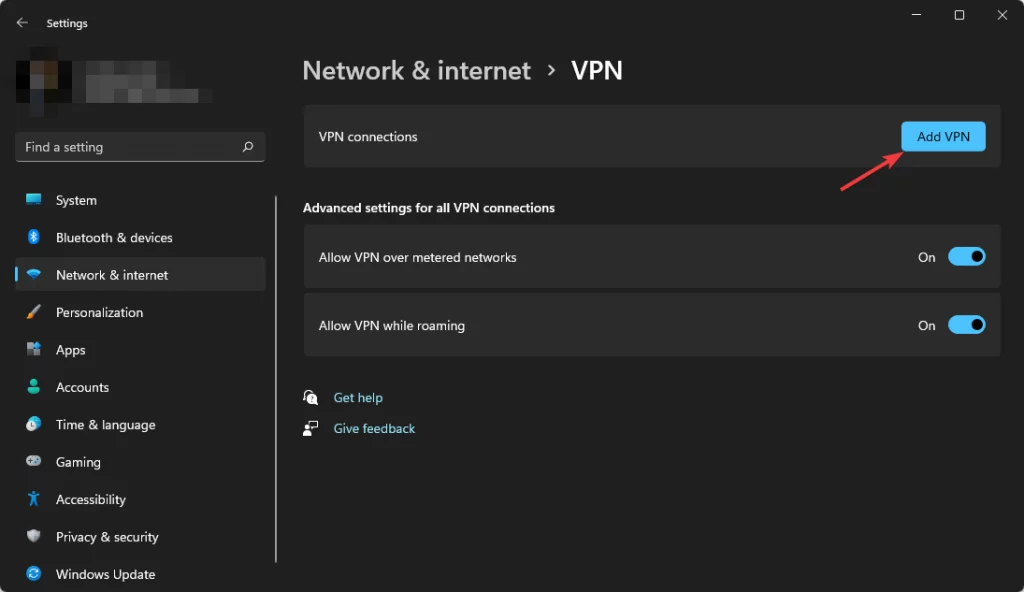
Go to Settings → Network & Internet → VPN → Edit.
Make sure VPN type is set to “L2TP/IPsec with pre-shared key.”
Re-enter your PSK, username, and password.
Verify the server address is correct and active.
For extra guidance, see how to connect to a VPN.
2. Start Required Windows Services
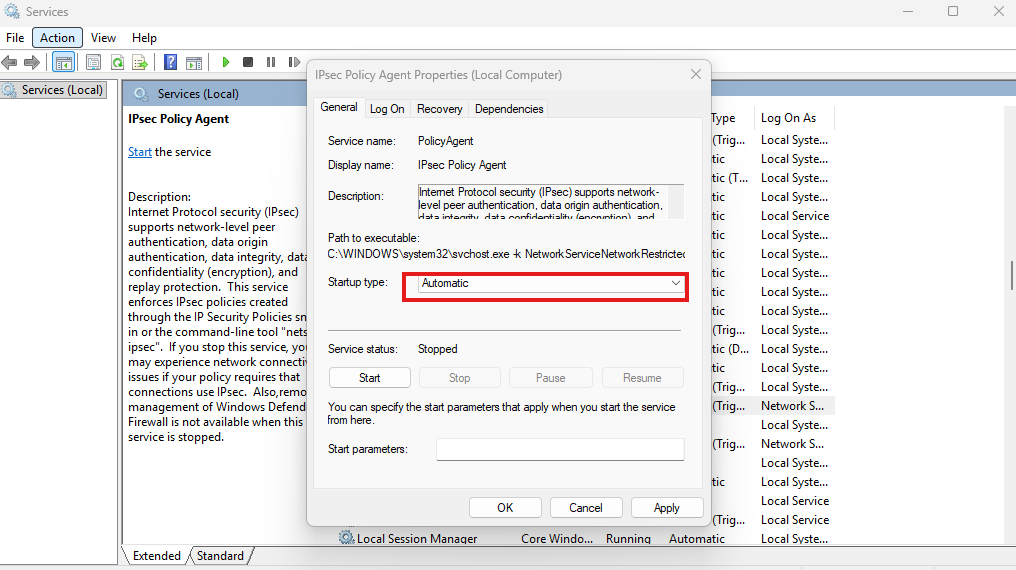
Press Win + R, type services.msc, and press Enter. Start and set to Automatic:
- IPsec Policy Agent
- IKE and AuthIP IPsec Keying Modules
Restart the PC and test again.
3. Allow VPN Ports and Protocols
On your firewall or router, allow:
- UDP 500 for IKE negotiation
- UDP 4500 for NAT traversal
- UDP 1701 for L2TP tunneling
- IP Protocol 50 for ESP
In Windows Defender Firewall, add inbound rules for UDP 500 and 4500 and a custom rule for ESP.
4. Enable NAT Traversal for VPN Connections
Open regedit and go to:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\PolicyAgent
Right-click → New → DWORD (32-bit) Value → name it AssumeUDPEncapsulationContextOnSendRule.
Set the value to 2 and restart the computer. This allows VPNs to work through most routers and fixes many Error 809 cases.
5. Reinstall WAN Miniport Adapters
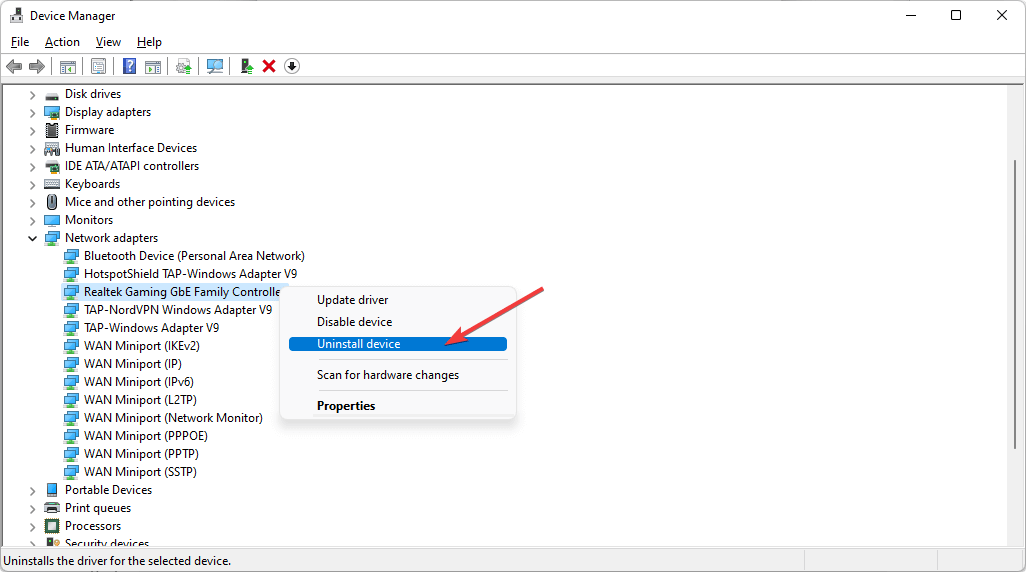
Open Device Manager → Network adapters. Uninstall:
- WAN Miniport (L2TP)
- WAN Miniport (IP)
- WAN Miniport (IKEv2)
Click Action → Scan for hardware changes. Windows will reinstall clean versions. If your VPN entry is missing from the list, use this fix for VPN not showing up in Network Connections.
6. Turn Off IPv6 Temporarily
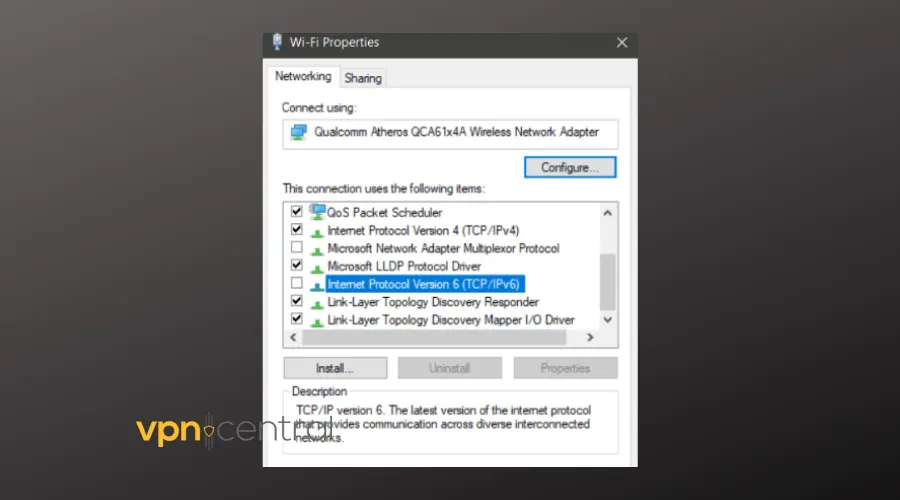
Press Win + R, type ncpa.cpl, right-click your connection, select Properties. Uncheck Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6), click OK, and test again.
7. Pause Antivirus or Firewall Protection
Disable any third-party antivirus or firewall for a short test. If the VPN connects, add exceptions for UDP 500, UDP 4500, and ESP, then turn protection back on.
8. Check VPN Server Configuration
Confirm with your provider or admin:
- The server supports L2TP/IPsec with a PSK
- The PSK is correct
- Your account has permission
Try the same credentials on another device to see if the issue is local to your PC.
9. Remove Problematic Windows Updates
Open Settings → Windows Update → View update history → Uninstall updates. Remove updates installed right before the VPN stopped working. Reboot. Install newer fixes after the VPN works again.
10. Fix VPN IP Conflicts
Make sure your router’s subnet, for example 192.168.1.x, is different from the VPN’s internal network. Overlapping networks break routing. To confirm that internal resources are reachable, see how to access files through a VPN on Windows 10.
11. Reset Network Settings in Windows 10
Go to Settings → Network & Internet → Status → Network reset → Reset now. Reboot and set up the VPN again.
12. Update Network Drivers
Open Device Manager → Network adapters, right-click your Ethernet or Wi-Fi card, and choose Update driver → Search automatically.
13. Flush DNS and Reset Winsock
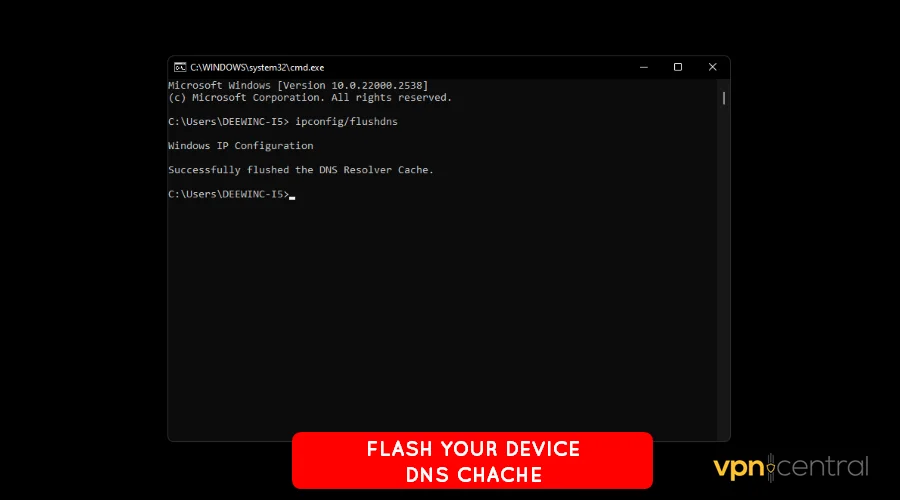
Open Command Prompt as Administrator and run:
ipconfig /flushdns
netsh winsock reset
netsh int ip reset
Restart the PC and test again.
14. Check the Event Viewer for VPN Errors
Press Win + X → Event Viewer → Windows Logs → Security or System. Look for Event IDs 20227 or 20209 for details on failed auth or missing services.
15. Create a New VPN Profile
Delete the old VPN profile and recreate it by hand. This clears hidden corruption or wrong parameters.
16. Change DNS Settings
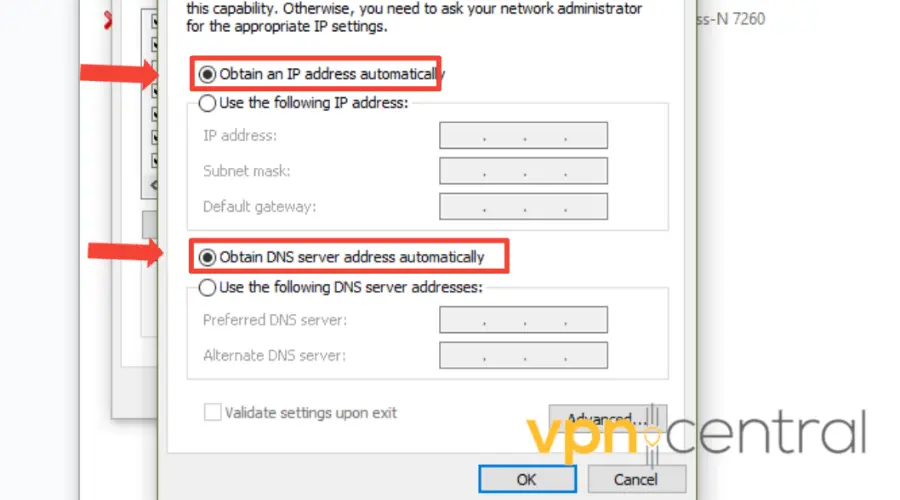
If the VPN connects but browsing fails, switch to public DNS. Try Google (8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1).
17. Update Router Firmware
Update the router firmware or enable VPN passthrough. Older routers can drop IPsec packets.
18. Test with a Different Network
Connect from another Wi-Fi or a mobile hotspot. If it works there, your main network or ISP is likely blocking IPsec.
Common Reasons Why L2TP/IPsec VPN Stops Working
- Wrong pre-shared key or credentials: One wrong character blocks the handshake.
- Authentication mismatch: The server may require a different protocol. See VPN protocols and authentication types.
- Firewall or NAT blocking: Missing UDP 500, 4500, or ESP permissions.
- Disabled IPsec services: IPsec Policy Agent or IKE modules are stopped.
- Corrupted network adapters: WAN Miniports damaged or missing.
- NAT traversal disabled: Registry key not set to
AssumeUDPEncapsulationContextOnSendRule=2. - Security software interference: Third-party tools blocking IPsec.
- IPv6 conflicts: Dual-stack routing issues.
- Windows update bugs: Some updates have broken L2TP/IPsec until later fixes.
Quick Reference: L2TP/IPsec VPN Error Codes and Fixes
| Problem | Fix |
|---|---|
| Wrong PSK or login | Re-enter credentials and PSK |
| Error 809 | Enable NAT traversal registry key |
| Error 789 | Allow UDP 500/4500 and ESP, start IPsec services |
| Error 766 | Switch to PSK instead of certificate |
| Connects but no traffic | Fix subnet conflict or turn off IPv6 |
| Error 720 | Reinstall WAN Miniports |
| Error 20227 | Check IPsec Policy Agent and IKE modules |
FAQs About L2TP/IPsec VPN on Windows 10
Some Windows updates have broken IPsec. Uninstall the latest update or install Microsoft’s follow-up patch.
Yes, but both client and server must be set up for certificates. If one side uses a PSK and the other expects a certificate, it fails.
Yes. Some updates caused similar L2TP issues. The same fixes usually apply.
Yes, with strong encryption like AES-256 and SHA-2. If possible, consider IKEv2 or OpenVPN for better reliability through NAT.
Final Verdict: Fixing L2TP/IPsec VPN Problems on Windows 10
Most issues come from a wrong pre-shared key, blocked ports, or NAT problems. Work through the fixes in order and test after each one. If the VPN still will not connect, contact your provider. The problem may be on the server side.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more





User forum
0 messages