LLM-Generated Passwords Show Predictability, Repetition, and Low Entropy Flaws

Large language models generate weak passwords despite complex appearances. A password like G7$kL9#mQ2&xP4!w looks random. Research proves it repeats often. Standard strength meters miss these flaws completely.
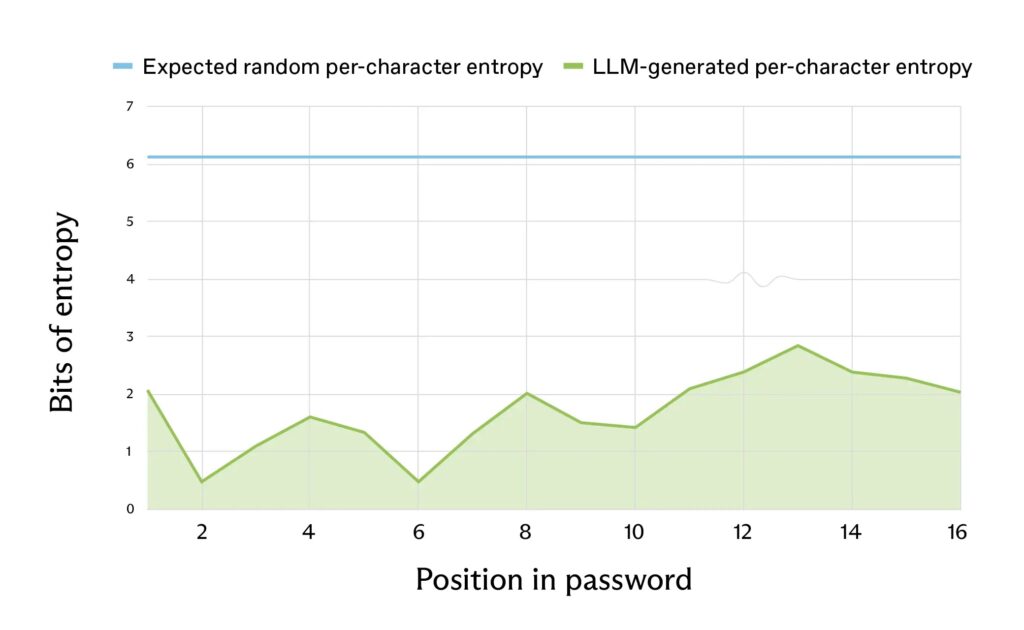
LLMs predict next characters based on training data patterns. This clashes with true randomness needed for security. Cryptographic generators pick each character equally. LLMs favor likely sequences instead. The result lacks real entropy.

Access content across the globe at the highest speed rate.
70% of our readers choose Private Internet Access
70% of our readers choose ExpressVPN

Browse the web from multiple devices with industry-standard security protocols.

Faster dedicated servers for specific actions (currently at summer discounts)
Researchers tested GPT, Claude, and Gemini models. Claude Opus 4.6 repeated one password 18 times in 50 runs. GPT-5.2 passwords mostly started with “v.” Gemini Flash favored “K” or “k” beginnings. These biases make cracking easy.
Coding agents embed these passwords in software automatically. Developers miss them in fast “vibe-coding” workflows. Production systems then hold predictable credentials.
“Claude Opus 4.6 generated only 30 unique passwords from 50 runs, with 36% probability for one sequence.”
Password Entropy Comparison
| Generator Type | Expected Entropy (16 chars) | Actual LLM Entropy |
|---|---|---|
| CSPRNG (Secure) | 98 bits | N/A |
| Claude Opus 4.6 | N/A | 27 bits |
| GPT-5.2 (20 chars) | N/A | 20 bits |
Low entropy means seconds to crack on normal hardware.
Model-Specific Patterns
| Model | Common Prefixes | Repetition Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Claude Opus 4.6 | G7$, K7#m | 36% single password |
| GPT-5.2 | vXXX | 80% start with v |
| Gemini 3 Flash | K, k | 65% K/k starts |
Patterns persist across temperature settings from 0.0 to 1.0.
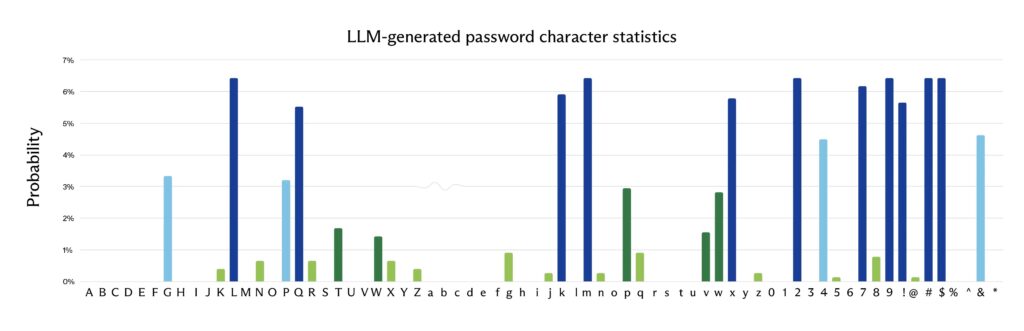
Character Distribution Flaws
LLMs show position-based biases:
- Position 1: Uppercase letters dominate (78%).
- Positions 2-4: Numbers and symbols cluster.
- Final positions: Predictable !@# endings (42%).
True random spreads evenly across all positions.
Real-World Risks
Weak passwords hit production via:
- AI coding agents inserting creds silently.
- Developers accepting “helpful” generations.
- Vibe-coding skipping code review.
GitHub holds leaked LLM prefixes like K7#mP9.
Mitigation Checklist
Secure coding requires these steps:
- Disable LLM password generation prompts.
- Use openssl rand or /dev/random in scripts.
- Audit AI-generated code for hardcoded secrets.
- Rotate all potentially LLM-created passwords.
- Measure entropy with zxcvbn library.
Enforce CSPRNG in DevOps pipelines.
Attack Scenarios
Predictable patterns enable:
- Dictionary attacks with model-specific wordlists.
- Rainbow tables for common prefixes.
- Brute-force reduced to minutes.
Services with LLM-set passwords face mass compromise.
Detection Tools
Scan for LLM fingerprints:
- High repetition across user accounts.
- Prefix clustering (vXXX, K7#m patterns).
- Entropy below 4 bits per character.
Password audit tools flag these automatically.
FAQ
Prediction bias creates patterns, not true randomness.
Claude Opus 4.6 repeated one password 36% of time.
No. Max temperature 1.0 still shows patterns.
98 bits minimum. LLMs deliver 20-27 bits.
Insert credentials during autonomous development.
openssl rand, /dev/random, or CSPRNG libraries.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more





User forum
0 messages