What Is the Wireguard VPN Protocol? [A Beginner's Guide]

WireGuard is supposed to be the future of VPN tunneling. The fact that more and more VPN applications are supporting it is proof that it’s moving in the right direction.
But what makes it so attractive?
Is there anything to worry about?
Let’s unpack what this VPN protocol is all about!
What is the WireGuard VPN protocol?
The WireGuard VPN protocol is fast and easily deployable. It transmits encrypted traffic over a VPN in a swift manner without compromising security.
WireGuard gets praised for being as fast as various outdated protocols minus their susceptibility to attacks. At the same time, it’s not as complicated to configure as current standards like Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) and OpenVPN.
Initially rolled out for Linux, it’s now cross-platform, thanks to it being open-source. As of now, it also supports Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and BSD.
Although it’s only been around since 2015, it’s quickly shaping up to dethrone OpenVPN as the dominant VPN protocol.
How does WireGuard work?
Generally, WireGuard works by using ChaCha20 for encryption and Poly1305 for data authentication. This cryptographic choice is a bold departure from conventional VPN practices that emphasized AES-256.
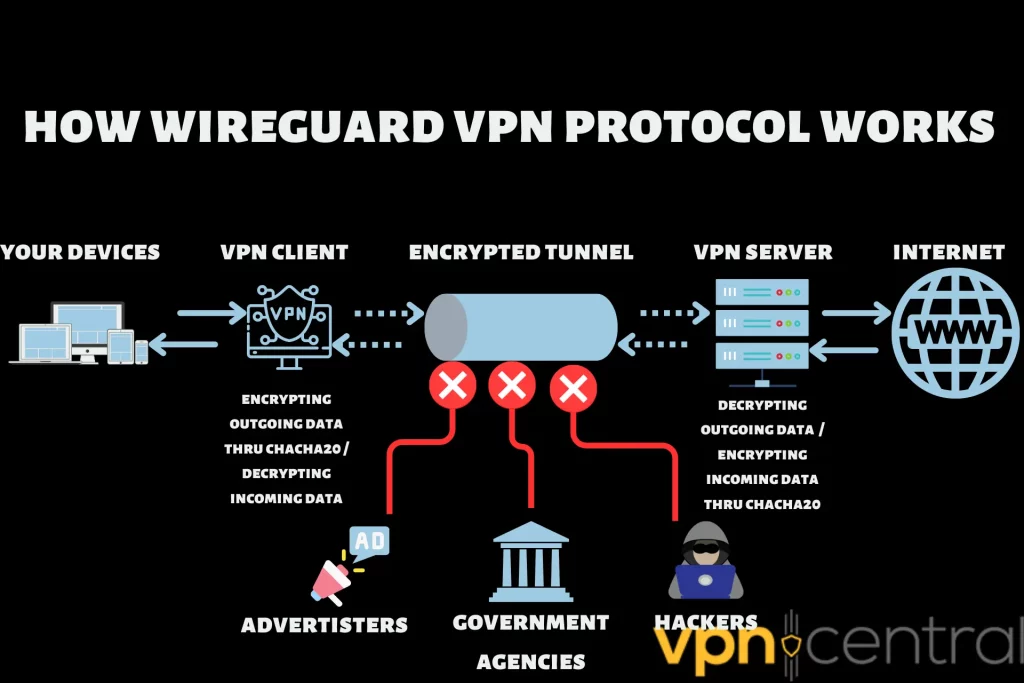
Theoretically, ChaCha20 is more prone to brute-force attacks because of its short key length. However, the longer encryption key of AES-256 can be overkill, noticeably slowing down your internet speed. Conversely, ChaCha20 is uncrackable and doesn’t cause significant speed drops.
Furthermore, WireGuard only tunnels traffic over User Datagram Protocol (UDP). In other words, it skips additional verification measures to move the data from point A to B more quickly.
Is WireGuard secure?
WireGuard is secure for four reasons:
- Cutting-edge encryption
- Open-source nature
- Minimal code
- Easy implementation.
Let’s throw more light on each of them.
Cutting-edge encryption
Besides ChaCha20, WireGuard also supports other modern encryption protocols such as Curve25519 and SipHash24. It doesn’t use any obsolete method to scramble your data, making it virtually unhackable.
Admittedly, novelty is one of the reasons why WireGuard enjoys a solid reputation from a security standpoint. Ethical hackers could discover major flaws in its encryption methods down the road. Until then, there’s no reason to doubt this VPN protocol’s resistance to cyber-attacks.
Open-source nature
WireGuard lends itself to constant scrutiny. Its code is available for public consumption. So, the entire cybersecurity research community can study it and collectively address its bugs.
Minimal code
WireGuard’s codebase is just a fraction of OpenVPN’s, 4,000 versus 400,000 lines. Because of this, white-hat hackers can audit it more easily and black-hat ones only have a tiny attack surface to exploit.
Easy implementation
Compared to OpenVPN and IPSec, WireGuard is much less susceptible to misconfiguration. To begin with, its design is incredibly streamlined. The less complicated it is to implement, the less likely VPN vendors are to make mistakes when setting it up.
WireGuard pros and cons
Just like any VPN protocol, WireGuard has pros and cons. Here’s the number one reason why it’s so appealing and the main drawback to it.
Biggest advantage: Speed
Nothing’s faster than WireGuard. It hardly has any negative impact on base internet speeds. Additionally, it can help you minimize lag when gaming and streaming.
The reason behind this is the lack of handshake authentication due to its use of UDP.
On the contrary, OpenVPN involves a cumbersome data exchange process when in Transmission Control Protocol mode, which slows down speed.
What’s more, WireGuard’s lightweight design doesn’t consume lots of hardware resources. As a result, it can reduce the load times of other programs and enhance user experience.
Worst disadvantage: Privacy
The most common knock on WireGuard’s trustworthiness is its inability to dynamically assign IP addresses. It requires the server to have a table of local static IPs to manage the flows of internet packets. In other words, WireGuard depends on a user identity checklist to function.
For this reason, this speedy VPN protocol can’t always get around firewalls. If you need to access certain content from a repressive country or territory, WireGuard can’t obfuscate your data like OpenVPN. Even worse, it may expose your VPN use to your employer, the authorities, and other parties.
Thankfully, adopters of WireGuard work hard to overcome this weakness. An excellent case in point is NordVPN. This VPN vendor developed its own protocol around it called NordLynx. It uses a double Network Address Translation (NAT) system to eliminate the need to store traceable data on VPN servers.
Related articles:
What VPN services use WireGuard?
The list of VPN services that use WireGuard is growing. Apart from NordVPN, here are the other adopters of WireGuard:
- CyberGhost
- Private Internet Access (PIA)
- Surfshark VPN
- Proton VPN
- PrivadoVPN
- Hide.me
- PureVPN
- IPVanish
- VyprVPN
Summary
So, what is the WireGuard VPN protocol? Arguably, it offers the most balanced trade-off between speed and security, making it suitable for most VPN uses. Although its privacy remains questionable, it has definitely provided a blueprint for what a new industry-standard protocol should look like.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more





User forum
1 messages