VPN vs Proxy: Which One Should You Use?
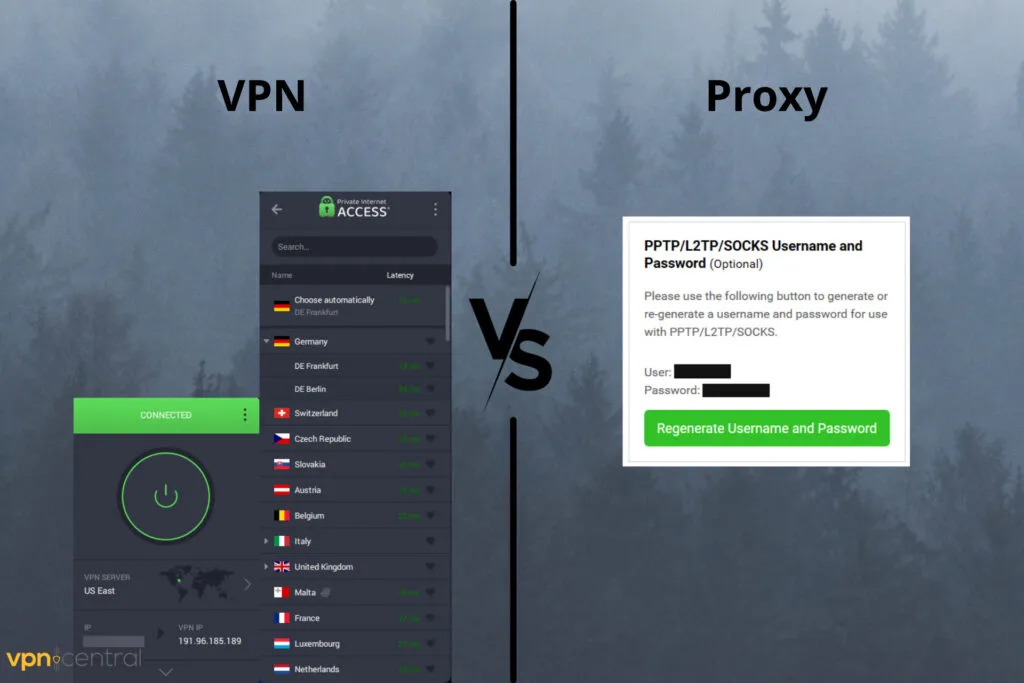
When it comes to online privacy and bypassing restrictions, many people wonder about the differences between VPN vs Proxy. Both tools hide your IP address and help you access blocked content, but they don’t work the same way. Understanding how they compare will help you choose the right option for streaming, security, and everyday browsing.
Table of contents
Is a VPN the same as a proxy?
No. A proxy forwards specific app or browser requests and swaps your IP, usually without encryption. A VPN encrypts all device traffic, routes it through a secure tunnel, and replaces your IP at the network level. That system-wide coverage and encryption make VPNs harder to detect and better for privacy.
Streaming platforms use aggressive blocking. Premium VPNs rotate IPs and add traffic obfuscation, which improves access. Proxies often fail those checks. If you want a quick primer on capable options, see this overview of VPNs with strong unblocking performance.
VPN vs Proxy by use cases
| Use case | Best choice | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Bypass geo-blocks on streaming (Netflix, Hulu, BBC iPlayer) | VPN | VPNs encrypt and mask traffic system-wide and rotate IPs, which defeats most streaming firewalls. |
| Open blocked sites at school/work | Proxy (or VPN if available) | Proxies reroute browser traffic fast. If admins block proxies, a VPN works more reliably. |
| Stay safe on public Wi-Fi | VPN | VPN encryption shields logins, messages, and DNS requests from snoops. |
| Torrenting / P2P | VPN | VPNs hide your IP and encrypt P2P traffic, reducing throttling and exposure. SOCKS5 hides IP but doesn’t encrypt. |
| Hide IP for casual browsing | Proxy | App-level IP masking feels lightweight and quick for low-risk tasks. |
| Shop or compare prices in other regions | VPN | Full-tunnel routing makes location spoofing more consistent for flights, games, or subscriptions. |
| Reduce ISP tracking | VPN | ISPs see only the encrypted tunnel, not your destinations or queries. |
| Scraping, automation, multi-account management | Proxy | App-scoped routing and large proxy pools suit high-volume, low-security tasks. |
When to use a VPN
Choose a VPN when you need privacy, reliable access, and protection everywhere on the device. Also see our detailed comparison of VPN vs Wi-Fi security risks to understand how different connection types expose you online.
- Bypass geo-blocking: Unlock websites, apps, streaming services, and games worldwide.
- Bypass censorship: Reach blocked services in restrictive regions.
- Browse anonymously: Mask your ISP-assigned IP address.
- Protect sensitive data: Encrypt traffic to stop hackers, trackers, and surveillance.
- Use public Wi-Fi safely: Prevent credential and session theft.
- Prevent throttling: Hide activity patterns that trigger slowdowns.
- Find better deals: Compare regional prices for flights, games, and subscriptions.
Top VPNs also add features proxies don’t offer:
- Kill switch: Cuts internet if the VPN drops to prevent leaks.
- Split tunneling: Route some apps through the VPN and others direct.
- Obfuscation: Disguises VPN traffic to bypass censorship in countries like China.
- Dedicated IPs: Avoid CAPTCHAs, blacklists, and account flags.
When to use a proxy
A proxy is lighter and often free. It can help when you only need IP masking in a browser or app without extra security. If pages won’t load or connections drop, follow our guide on how to check proxy and firewall settings to fix local blocks.
- Bypass geo-blocking: Simple website restrictions.
- Surf anonymously: Swap your IP for casual browsing.
- Stop throttling (limited): Hide some activity patterns from ISPs.
- Save money: Free proxies are common, but usually overloaded and insecure.
Which is better: VPN or proxy?
If all you need is to unblock a website quickly, a proxy works. If you want privacy, security, or to access content consistently, a VPN is better. VPNs offer system-wide encryption, reliable streaming access, and extra tools like kill switches and split tunneling. Proxies give only basic IP masking. For a broader look at how VPNs stack up against other network technologies, see our full guide on VPN vs VLAN.
Final thoughts
Both VPNs and proxies hide your IP, but they’re not equals. A proxy is lightweight and good for app-specific IP masking. A VPN encrypts everything, protects you on public Wi-Fi, and works better for streaming and torrenting. For most users, a VPN is the stronger choice.
👉 If you need a reliable all-rounder, consider premium VPNs such as ExpressVPN or PIA, which deliver strong encryption, fast servers, and effective geo-unblocking.
Having trouble making VPNs and proxies work together? Check our guide on how to fix Every Proxy not working with VPN.
For readers comparing VPNs with cloud-based setups, we also have a full guide on VPN vs VPC that explains how private networks differ from virtual private clouds.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more






User forum
0 messages