VPN vs Proxy: Are They the Same or Is VPN Better Than Proxy?
26 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more
Today, geo-blocking, anonymity, privacy, and security are issues of main concern for many Internet users like you, and that is for good reason.
Whether you simply want to access geo-restricted content regardless of your location or surf the web anonymously, privately, and securely, you can fully or partially achieve these with the use of a tool like a VPN or proxy server.
However, when it comes to choosing the right option, you might find yourself in a dilemma, as chances are that you – like many others – think the two options are very similar and have the same purpose, and thus you can use any of them without seeing any difference.
This is actually wrong. While both services allow you to bypass geo-blocking and surf the web anonymously, there are major differences between the two.
A proxy server is very limited in many areas compared to a Virtual Private Network (VPN) – which ensures full online security and privacy through encryption, among other things.
Continue reading to find out in what areas they differ and where they are similar, which one is the ideal solution and when.
Is VPN the same as a proxy?
No. Even though they have a common purpose and both hide your locations, there are key differences between VPNs and proxies. Both can spoof your whereabouts.
By spoofing your location, you will be able to circumvent geo-restrictions, namely, access online content that is unavailable in your geographical area or country.
But when it comes to strict blocks, VPNs are the better solution. However, not all services manage to unblock everything.
For example, popular streaming services such as Netflix have proxy detection systems that can detect VPN use, in which case you will be denied access to the service.
In addition to allowing you to bypass geo-blocking, a VPN also takes care of your online anonymity, privacy, and security with encryption. Proxies don’t typically use encryption.
VPN vs Proxy – how do they compare?
A VPN masks your ISP-assigned IP address and replaces it with a new one from a location where the VPN server resides. Proxies do similar things but don’t encrypt data.
The VPN ensures complete privacy and protection for all of your connected devices by encrypting your entire traffic and rerouting it through a secure VPN tunnel.
Unlike a proxy – which only provides anonymity and lets you bypass geo-restrictions – a VPN comes with enhanced privacy and security as well as other useful features that we’ll describe below.
VPN – best solution for security, privacy, and bypassing geo-blocking
How does a VPN work?
Both a VPN and proxy will get you a new IP address from a new virtual location. So, when you’re surfing the web, the websites and services you access will see an IP coming from the virtual location instead of your current physical one.
Nonetheless, there are VPN products that have strong unblocking capabilities and work very well with streaming services as well as other types of online content for that matter.
Therefore, you can go about your casual online business carefree, without worrying about cyberattacks, tracking, monitoring, or third-party surveillance.
There are two types of VPNs, namely, corporate VPN and individual VPN. The former is used by businesses to provide their employees secure access to cloud resources on a company network, whereas the latter is designed for individual use.
When can I use a VPN?
You can use a VPN service in many situations depending on your particular needs. Below, you can find the main reasons for which Internet users resort to VPNs.
- Bypass geo-blocking. Since a VPN allows you to connect to different servers across the globe and get a different IP from each, you will be able to access geo-restricted content such as websites, apps, streaming services, and games regardless of your physical location.
- Bypass censorship. Some countries have strong online censorship laws in order to block users from accessing certain websites and services. This is done based on your IP, but a VPN assigns you a new one, and thus you’ll manage to bypass any form of censorship.
- Surf anonymously. If you’re concerned about keeping your online identity anonymous while surfing the web, then you can easily achieve this with a VPN since it masks your ISP-provided IP, which represents the main online identification factor.
- Keep data private and secure. Due to strong encryption, a VPN secures all of your traffic and keeps your sensitive data private. Therefore, hackers, trackers, snoopers, ISP monitoring, government surveillance, etc. will be a thing of the past.
- Protect devices on public Wi-Fi. Whether you connect to a public WiFi in a café or airport, these networks usually have poor security, so your data may be vulnerable. Fortunately, when you connect to a VPN, no one can intercept your traffic.
- Prevent bandwidth throttling. Sometimes, your ISP may intentionally slow your Internet speed for various reasons. This is usually based on your online behavior. However, when you use a VPN, your ISP can no longer see what you do or where you go online.
- Avoid network restrictions. When you’re on a university campus, for example, the network may restrict you from accessing certain websites, streaming services, or online games. Nonetheless, a VPN allows you to change your IP so you won’t be blocked anymore.
- Get better price deals. Whether you want to buy games cheaper or get discounts on airline tickets, a VPN can help. These prices are tailored according to specific locations or regions. However, with a VPN, you can change your geo-location to get cheaper deals.
How to use a VPN?
Using a VPN is not complicated at all. All you need to do is decide on which product you want to choose and follow a few steps in order to configure the service on your device.
The steps may vary depending on the specific VPN you chose as well as the device (PC, laptop, smartphone, tablet, browser) and operating system (Windows, macOS, Android, iOS) you want to use it on.
While there are variations related to the aforementioned devices and platforms, the process itself is an easy one with every VPN service and does not require advanced technical expertise.
In the example below, we show you how to set up Private Internet Access (PIA) on a Windows computer.
- Get a subscription and download the VPN client.
- Install the client on your device and launch it.
- Go to the list of available servers and select one.
- Connect to the VPN server.
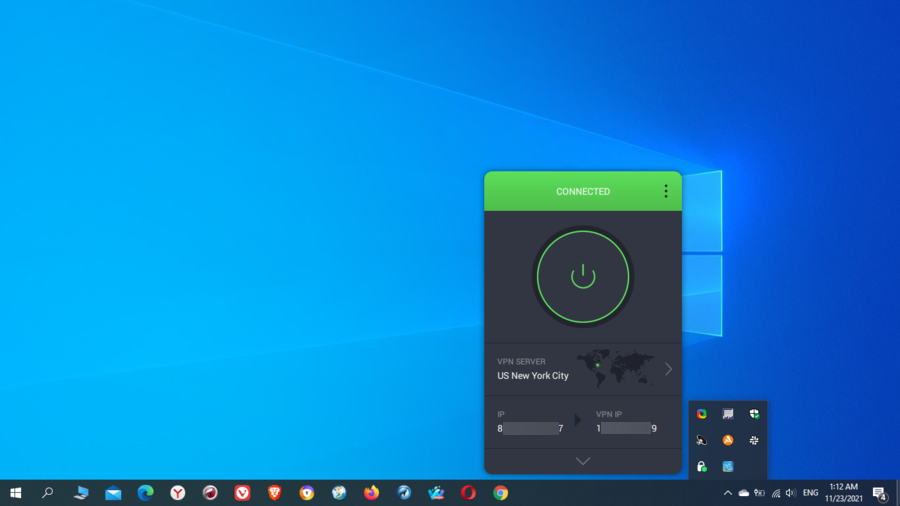
- Start surfing the web securely and privately.
If you want to use a reliable and well-reputed VPN service but you find it hard to choose the right one for you, then you might want to give Private Internet Access (PIA) a shot.
This VPN is trusted by millions of users worldwide and has an extensive network of servers distributed globally that will help you bypass geo-blocks in no time.
Moreover, it provides state-of-the-art security and privacy as well as other important features not available found with other VPN competitors.
You’ve already seen in the examples above the many great features PIA offers, so if you want to enjoy them too, feel free to try this VPN out.
More about PIA:
- 32,000+ servers in 101 locations across 78 countries.
- No traffic or request logs.
- Up to 10 simultaneous connections.
- Risk-free 30-day money-back guarantee.
- 24/7 live chat customer support.

Private Internet Access
Try PIA if you want to access geo-blocked content while also surfing anonymously, privately, and securely.What features do VPNs offer?
Servers
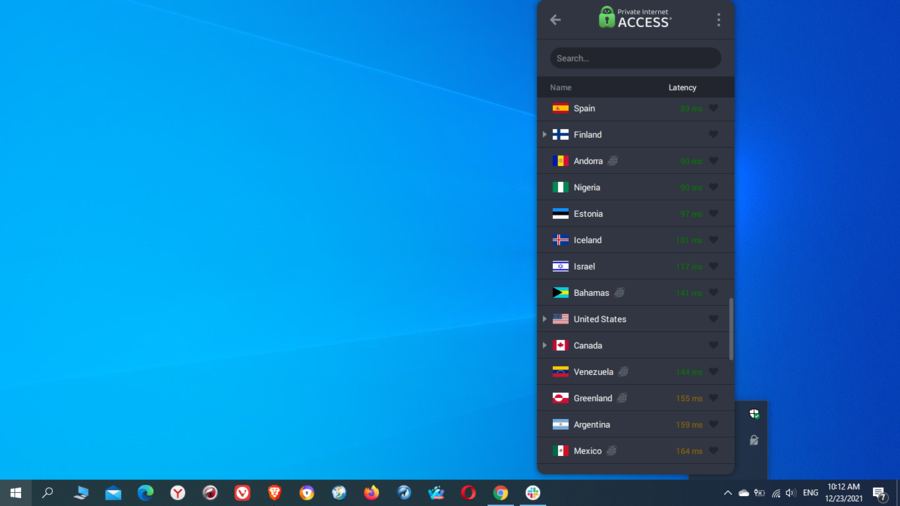
VPN servers represent one of the most important features when reviewing a VPN service, as they are the path by which users connect to different locations in order to get around geo-blocks.
Well-reputed VPNs provide extensive networks of fast VPN servers spread across multiple locations and countries all over the world. The more servers distributed over many locations, the more chances users have to access geo-restricted content.
Also, the quality of the VPN server infrastructure is very important. Servers need to be periodically updated, operated, and maintained at the highest standards to guarantee the best performance, privacy and security.
Speed
Speed plays a major role since it can significantly impact your overall online experience, whether it be surfing the web, watching content from streaming services, playing online games, or torrenting.
Of course, fast speeds are always desirable for the smoothest experience. Slow speeds, on the other hand, can be very annoying since they cause buffering and lagging, which can ruin your streaming and gaming sessions.
The main factor affecting speed in the case of VPNs is encryption. Since your traffic is rerouted via a secure tunnel, this adds extra steps between you and the Internet, which will slow your speed.
Nonetheless, with a reliable and top-notch VPN software, you won’t be affected to a great extent by the eventual decrease in speed. In fact, you may not even notice it while surfing.
The distance between your actual location and the VPN server can also affect speed. So, whenever possible, try to connect to a VPN location that is closer to your physical location.
In the examples below, we run two Internet speed tests using Speedtest by Ookla – a tool that analyzes performance metrics, such as upload speed, download speed, and ping.
Speed before connecting to the VPN
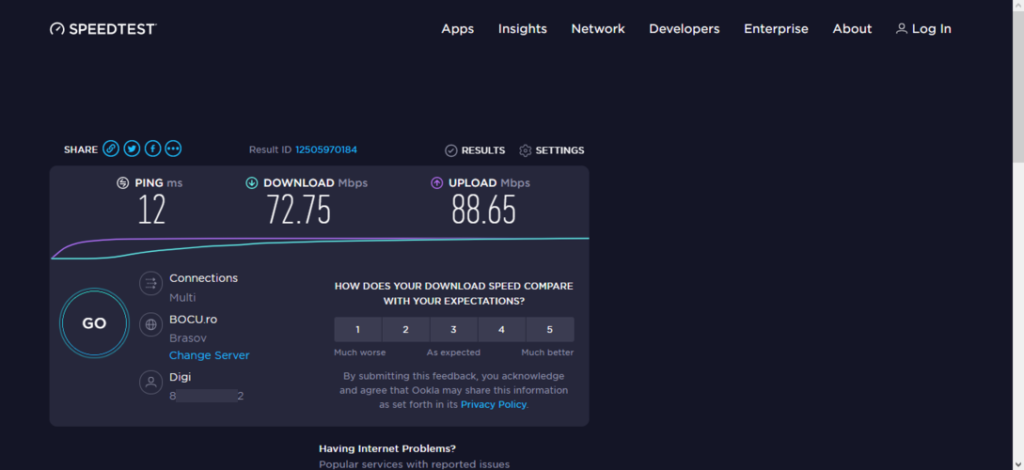
Here, we run the test while openly connected to the Internet from a location in Brasov, Romania.
Speed after connecting to the VPN
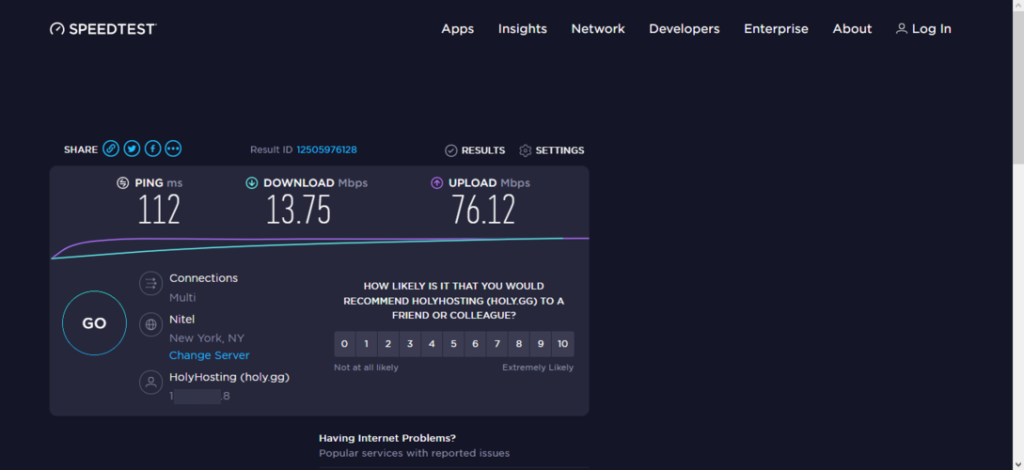
Here, we connected to a VPN server in New York, NY. The decrease in speed is understandable if we account for the large distance between Romania and the USA.
Encryption
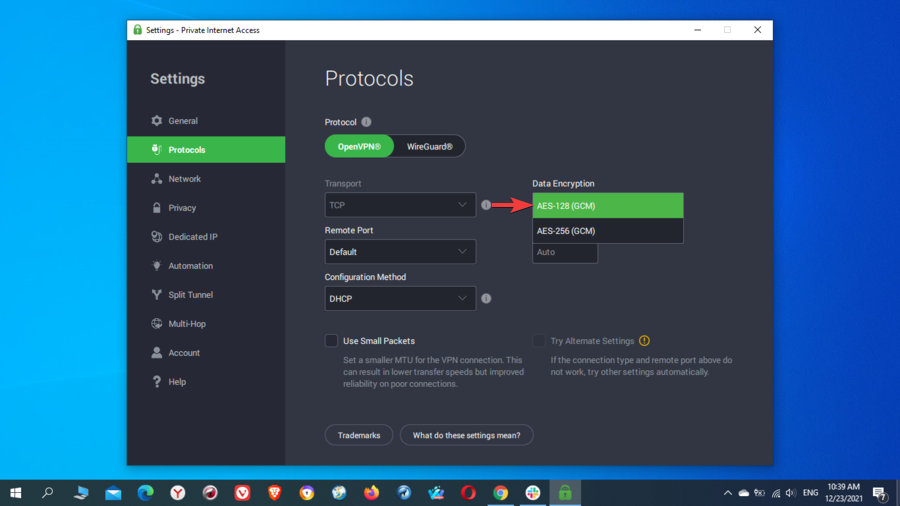
Encryption is of paramount importance for a VPN since it’s the feature responsible with ensuring your online privacy and security. That’s what actually distinguishes a VPN from a proxy server.
VPN encryption works by making the data that goes between your device and the VPN server unreadable to anyone else.
The data is converted from a readable format to an encoded, unreadable format with the help of an algorithm. Only the appropriate decryption key can decode the encoded format.
Encryption protects your sensitive data, such as login and banking credentials, from cybercriminals, and it also prevents tracking, monitoring, and surveillance by advertisers, ISP, or governments.
AES-256 is the industry standard military-grade encryption that intelligence agencies, governments, and militaries worldwide use.
AES stands for Advanced Encryption Standard and applies different cryptographic keys to a block of data. The keys come in three different lengths. Namely, 128, 192, and 256 bits, where the 256-bit key is the longest AES allows.
Consequently, it’s preferable that you use a VPN that uses nothing less than AES-256-bit encryption, as this is simply impenetrable even for the fastest computers.
Protocols
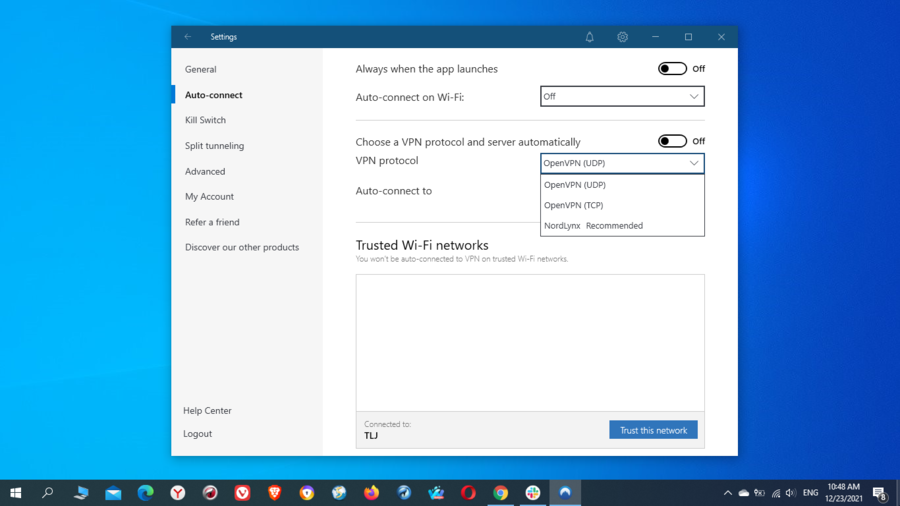
We’ve already covered that a VPN directs your traffic via an encrypted tunnel to a VPN server that will assign you a new IP address.
VPN protocols are sets of rules and processes that determine how your data routes between your device and the VPN server. In other words, they determine how the VPN secure tunnel is actually formed.
Among the most common VPN protocols, we have the following:
- PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
- L2TP/IPSec (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
- OpenVPN (TCP and UDP)
- SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol)
- KEv2/IPsec (Internet Key Exchange version 2)
- WireGuard (newcomer to the protocol world)
OpenVPN is the most popular VPN protocol among VPN providers, as it’s very secure and reliable. It runs on either UDP (User Datagram Protocol) or TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connection protocols.
WireGuard is the newest VPN protocol addition on the market and is already very promising since it’s very fast, uses advanced criptography, and has a very low attack surface.
Kill switch
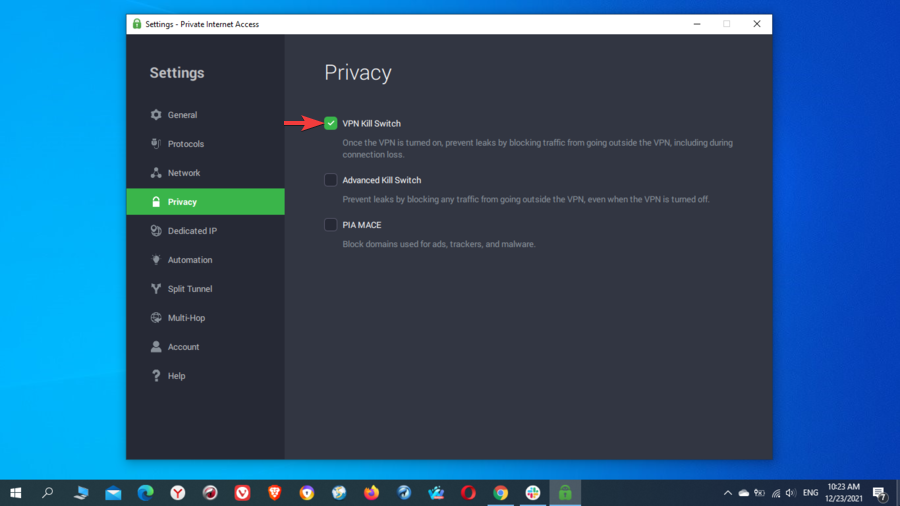
The kill switch is a very useful security feature that is not found with every VPN service out there, as only the best ones provide it.
The feature works by disconnecting your device from the Internet if your VPN connection drops unexpectedly. During that short period of time when the connection drops or when you switch between different networks, your device will remain unprotected.
However, if you enable the kill switch, the VPN shuts down the entire Internet connection in order to prevent any potential data leaks.
Depending on the VPN you’re using, you can choose to enable the kill switch for certain apps or system-wide. Also, not only can you enable the kill switch to do its job when the VPN is on but also when it’s off if you like. Thus, the VPN blocks any traffic that goes outside its tunnel.
Ad blocker
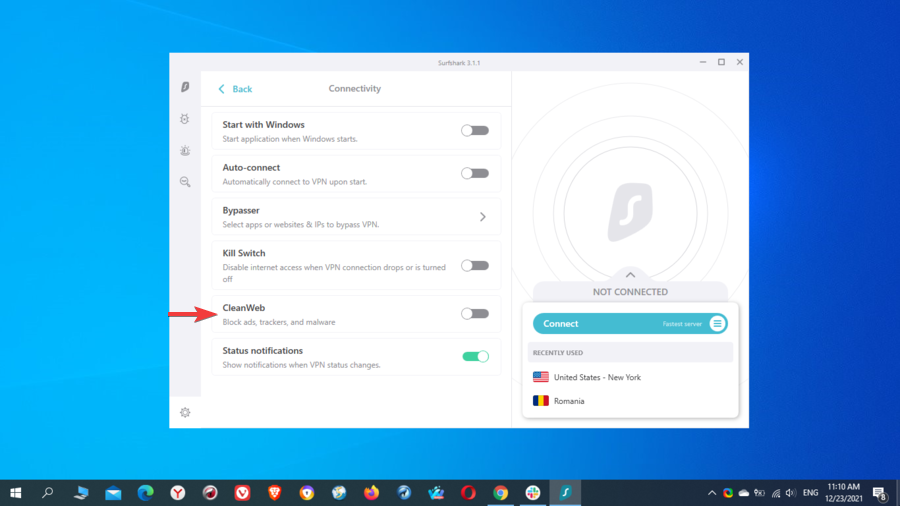
Some VPNs also include an ads and malware blocker that can be found under different names, but in general, all of them usually have the same purpose.
A VPN ad blocker can be very helpful since it takes your privacy and security to the next level by blocking ads, trackers, and websites that can host malware or phishing scams.
Split tunneling
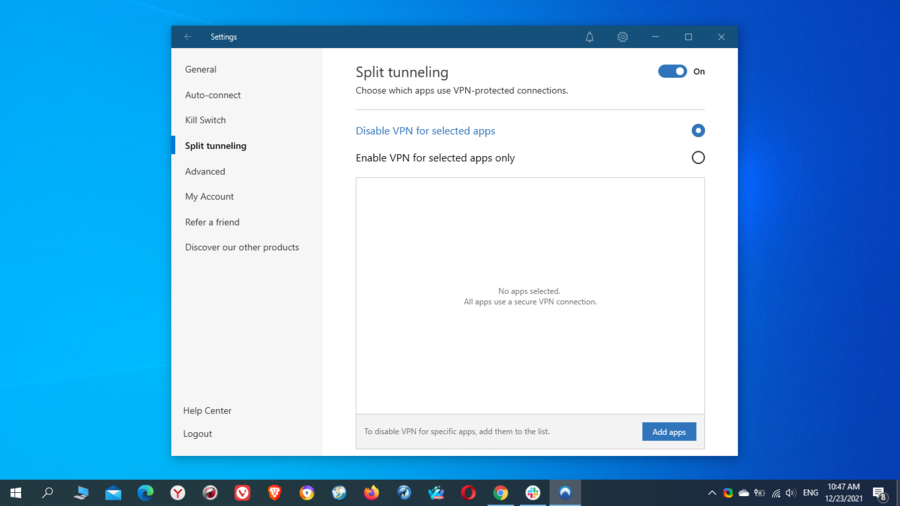
Split tunneling is a nice feature that allows you to route some of your traffic or apps through the VPN tunnel, while the rest will have direct access to the Internet.
This way, you can benefit from the advantages of a VPN, such as circumventing geo-blocking and surfing anonymously and securely while also being able to access local content.
For example, when you use the VPN system-wide, all of your traffic will be directed through the VPN tunnel, and you’ll get a different IP.
In this situation, you may lose access to certain websites or services in your own country, so instead of turning off the VPN entirely, you can designate rules to only use the it for specific browsers or apps.
Port forwarding
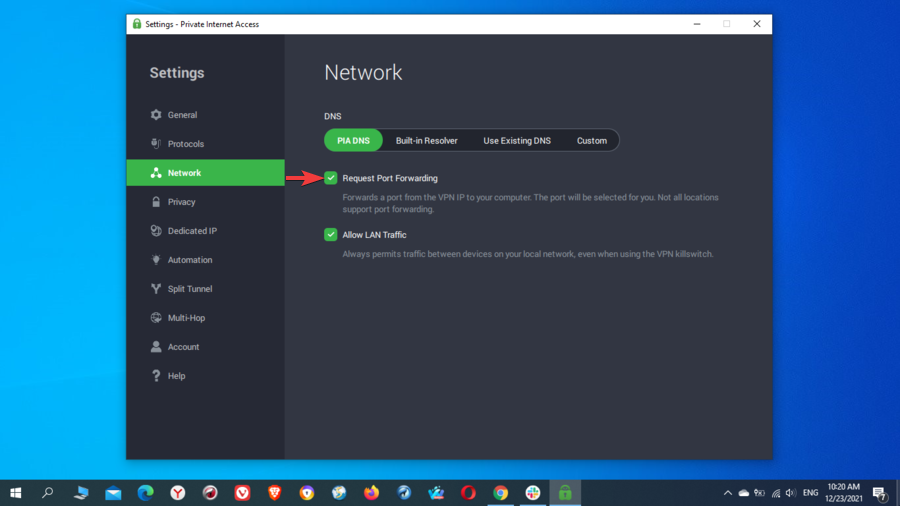
Port forwarding is a process that forwards the Internet data going to a certain port to another port. It’s a method that allows Internet traffic to go to a specific device more efficiently and quickly.
Certain VPNs use port forwarding as well. This is done by rerouting the incoming connections to get around the NAT firewall, which results in faster connection speeds.
Port forwarding can be useful, as it can increase download speeds, which are important for torrenting. Also, it lets you access your computer remotely when you’re away.
Multi-hop
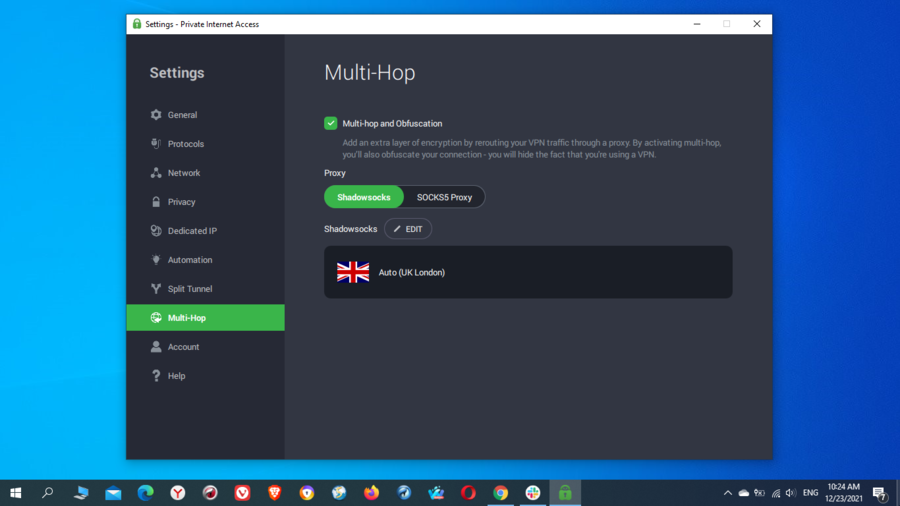
Multi-hop or double VPN – as its name suggests – adds an extra/double layer of security to your VPN by allowing you to connect and route your traffic via two VPN servers instead of one.
Since the VPN encrypts your traffic and data twice, you will benefit from extra security and privacy while conducting sensitive business online. Only a select few VPNs offer the feature.
Obfuscation
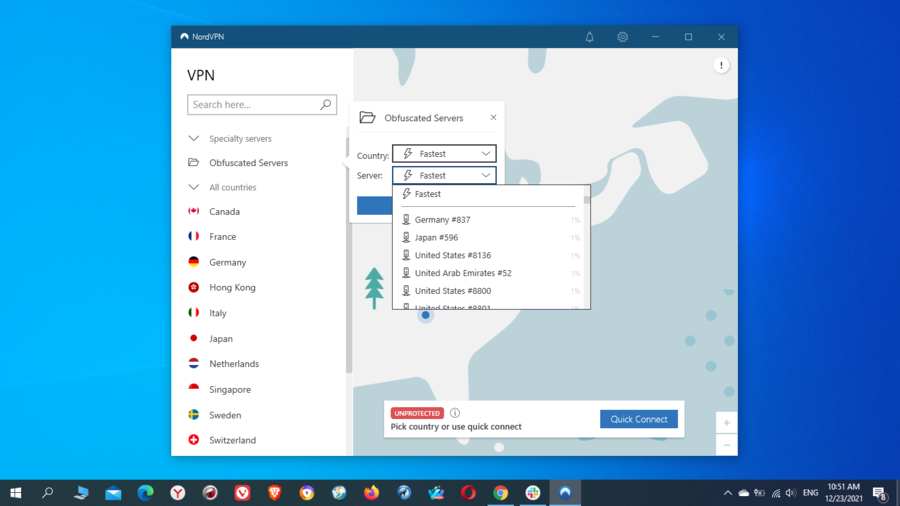
Obfuscation is a unique feature that you can enjoy with only a few premium VPN services. It is very useful since it allows you to bypass online censorship in heavy restricted environments.
Countries like China, Russia, Belarus, North Korea, Turkmenistan, Uganda, Iraq, Oman, Turkey, the UAE, etc. implemented a partial or complete ban on the use of VPNs, so using such a service there might be challenging, if not impossible.
Although a VPN hides your online identity and encrypts your connection so that no one can pry into your online affairs, your ISP will, however, know that you’re using a VPN.
So this is where obfuscation comes into place. When enabled, this mode hides the fact that you’re using a VPN by making your VPN traffic look like regular traffic. Therefore, your ISP will no longer know that you’re connected to a VPN.
Consequently, when you turn on obfuscation mode, you will manage to use a VPN in countries where the use of VPNs is tightly regulated or entirely banned.
Dedicated IPs
When you connect to a VPN server, you share your IP address with other users on the same server. Sometimes, you may experience slower speeds due to network congestion.
However, some VPNs allow you to get a dedicated IP that will be for your own use only. With a dedicated IP, you will enjoy faster speeds and see fewer CAPTCHAs since protection systems are less likely to think that you’re a bot.
Also, you will avoid security warnings that may lead to account restrictions by gaming or gambling platforms given that your IP is constantly changing.
Moreover, certain behaviors on the part of other users on the same VPN server may lead to IP bans, so with a dedicated IP, you shouldn’t worry about that as long as you maintain a decent online behavior.
P2P & torrenting
Many VPNs support P2P traffic and torrenting, so if you torrent regularly, you should use a VPN for security reasons.
Some VPNs have optimized servers for torrenting, which provide fast speeds. Thus, you can choose to connect to such servers for a smoother and faster torrenting experience.
Since torrenting is illegal in certain countries, using a strong VPN is the only way you can get around restrictions. Nonetheless, make sure to use it with caution.
Proxy – good for bypassing geo-blocking but lacks security and privacy
Unlike VPNs – which work system-wide in order to secure your entire network traffic – proxies only work on the application level, whether it be a specific browser or another app for that matter.
A proxy server works as a gateway or relay between your device and the websites you visit on the Internet. In other words, it is an intermediary server to which you can connect to hide your IP and spoof your location.
When you connect to a proxy server, your ISP-provided IP address is masked and replaced with a new one in a different location to which the host server belongs.
Thus, the websites, streaming platforms, apps, or games you’re trying to access will see an IP coming from the location of the proxy server instead of your current physical location.
There are proxy servers all over the world, so if you want to visit a restricted website or access content that is unavailable in your country, you can connect to a proxy server in a country or region where the specific websites and content are available.
How does a proxy work?
A proxy lest you both surf the Internet anonymously, and bypass geo-blocking thanks to its capability to conceal your real IP and allow you to change it.
Unfortunately, as previously mentioned, proxies only reroute traffic coming from a single browser or app you set them up with.
Moreover, unlike VPNs, they do not provide any kind of encryption to keep your data private and secure.
This means that your sensitive data might end up in the wrong hands, such as cyber criminals. Also, your traffic can be susceptible to active monitoring and surveillance by other unauthorized parties.
There are different types of proxy servers, three of the most common being the following:
- HTTP proxies – these proxies are only used to access websites from your browser. By configuring your browser to use a proxy server, you can access geo-blocked content since all the traffic going through that browser will also be directed via the proxy server.
- SOCKS proxies – work beyond the level of websites. In fact, they can be used on the app level with video streaming services, file-sharing sites, or online gaming platforms. However, they are slower than HTTP proxies due to higher loads and slower infrastructure.
- Transparent proxies – as their name implies – can be set up so that users do not know about their existence. In fact, you might have used one without realizing it. These proxies are used by companies or parents who want to monitor and filter Internet use.
When can I use a proxy server?
As with a VPN, you can use a proxy depending on what exactly you’re doing online. The following are the main situations in which you can use a proxy server instead of a VPN.
- Bypass geo-blocking. When you connect to a proxy, your IP will be masked and replaced with that provided by the proxy server. This will make your traffic appear to be coming from where the server is located; thus you can trick the system in order to bypass geo-blocks.
- Surf anonymously. Since a proxy hides your ISP-assigned IP address and provides you a new one in a different location, you’re no longer identifiable online based on your actual IP, meaning that you’ll manage to surf the web anonymously.
- Stop ISP throttling. Your ISP can throttle your bandwidth to control traffic and reduce network overload. However, since a proxy masks your IP, the content you’re viewing will no longer be associated with your ISP-assigned IP address but with that of the proxy.
- Save money. Unlike VPNs, you can easily get a proxy for free. So, if you’re on a shoestring budget, you may use a free proxy to save money. Nonetheless, keep in mind that this might come at a price in terms of privacy and security.
What features do proxies offer?
Apart from concealing your IP address and location in order to make you anonymous online and allow you to bypass geo-blocking, proxies do not offer the features described above that are found with top VPN providers.
The most important feature that is lacking with proxies is encryption – which provides enhanced online security and privacy. While you can mask your IP address to surf anonymously when connected to a proxy server, your traffic history and sensitive data are not private and secure.
The owners of the proxy server can intercept your traffic and data since they’re not encrypted. This makes you more susceptible to cyberattacks, tracking, spying, and government surveillance.
You might think that proxies offer faster speeds compared to VPNs because they don’t use encryption. While encryption does indeed reduce speed, it’s not the only factor that can affect it.
In the case of proxies – unlike VPNs – the majority of them are offered for free, meaning that anyone can gain access to a server with just a few clicks.
Since they are free, it’s obvious that many use them to bypass geo-blocking and access restricted content. When multiple users connect to the same proxy, this will lead to server overload, which in turn leads to slower speeds.
Below, we show you the results of two Internet speed tests that we run, one before connecting to a proxy server, and the other afterwards.
Speed before connecting to the proxy
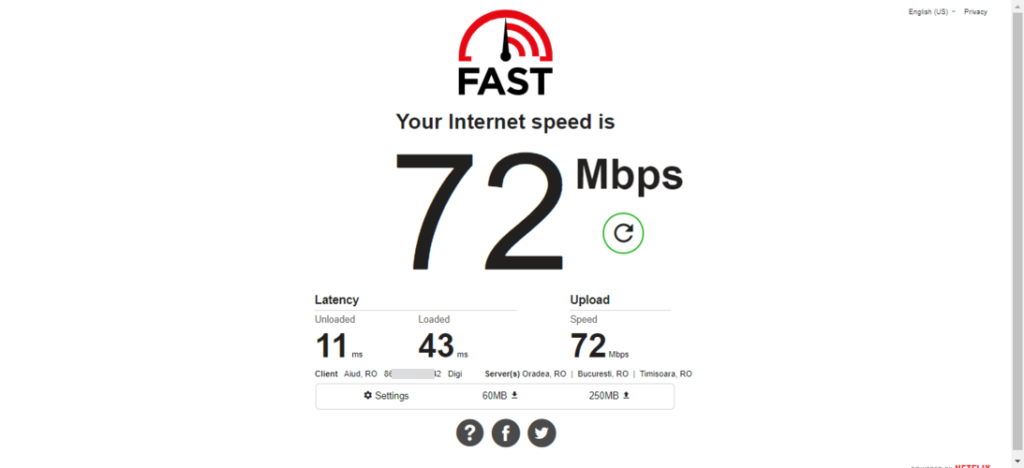
When we ran this test, we openly connected to the Internet from a location in Alba county, Romania. As you can see, the results were very good.
Speed after connecting to the proxy
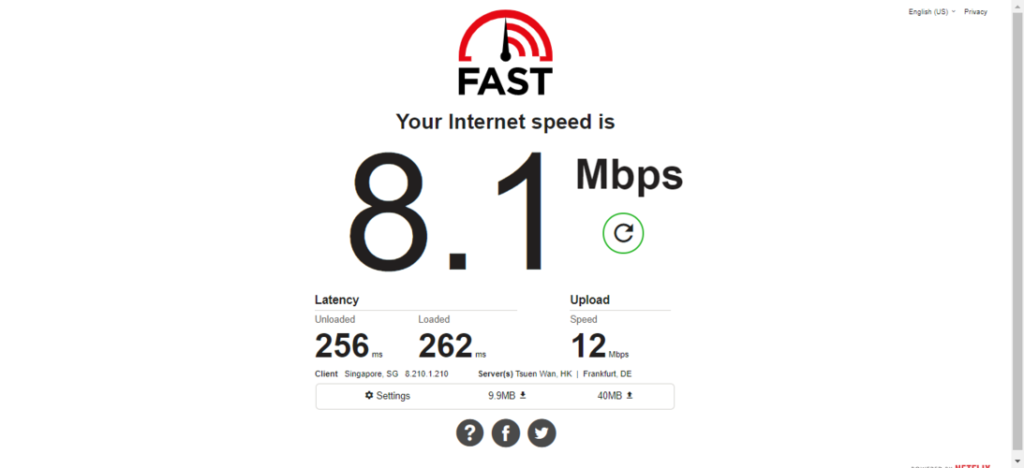
Here, we connected to a proxy server in Singapore. The speed is significantly lower. On the one hand, we need to account for the large distance between Romania and the proxy server location in Singapore.
On the other, there were probably plenty of other users connected to the server at the same time given that this proxy is free of charge.
The only way to avoid network congestion and get better speeds with a proxy server would be by buying a dedicated proxy, so only you can use it. This will also allow you to keep the same IP address all the time.
All in all, a proxy server falls short of providing as many features as a VPN does. In fact, it’s not even close to what a VPN offers. Thus, although proxies can be free or budget-friendly, they have limits in terms of what they can help you achieve online.
How to use a proxy?
Unlike a VPN, which you can easily set up on your device by simply installing the client that comes with all the necessary configurations in place, a proxy requires more steps to configure.
However, there’s nothing to worry about, as the process is quite simple. All you need to do is follow the steps for the appropriate situation below, and you should be ready to use the proxy right away.
As previously specified, proxies work on the application level, so each application supporting proxy setup can be configured separately to use the proxy.
However, with browsers such as Chrome, Opera, and Microsoft Edge, setting up a proxy comes along with other network settings. Exception to this is Firefox, which supports native proxy configuration.
In Windows 10, you can configure global proxy settings so that the proxy will apply system-wide. You can set up your proxy by selecting either automatic or manual proxy setup.
The former allows you to set up the proxy by specifying the script address provided by the network administrator or your company’s IT department, whereas the latter lets you set it up by manually entering its IP address and port number.
Alternatively, if you want to configure your proxy in Mozilla Firefox, you can follow the steps shown in the third example below. Before proceeding, make sure to have the proxy address and port number at hand.
Automatic proxy setup
- Go to Start and click on Settings.
- Click on Network & Internet.
- Click on Proxy, then go to the Automatic proxy setup section.
- Toggle on the Automatically detect settings option.
- Toggle on the Use setup script option.
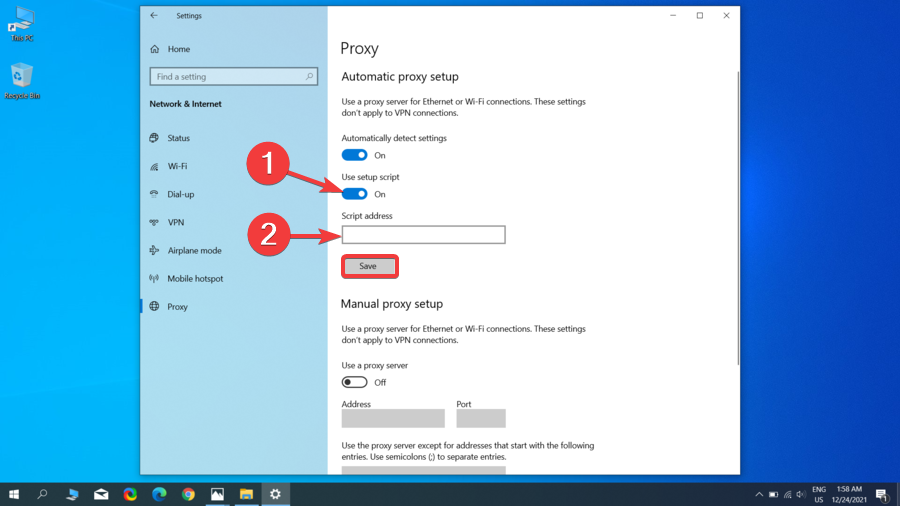
- Enter the Script address, then click Save.
Manual proxy setup
- Go to Start and click on Settings.

- Click on Network & Internet.

- Click on Proxy, then go to the Manual proxy setup section.
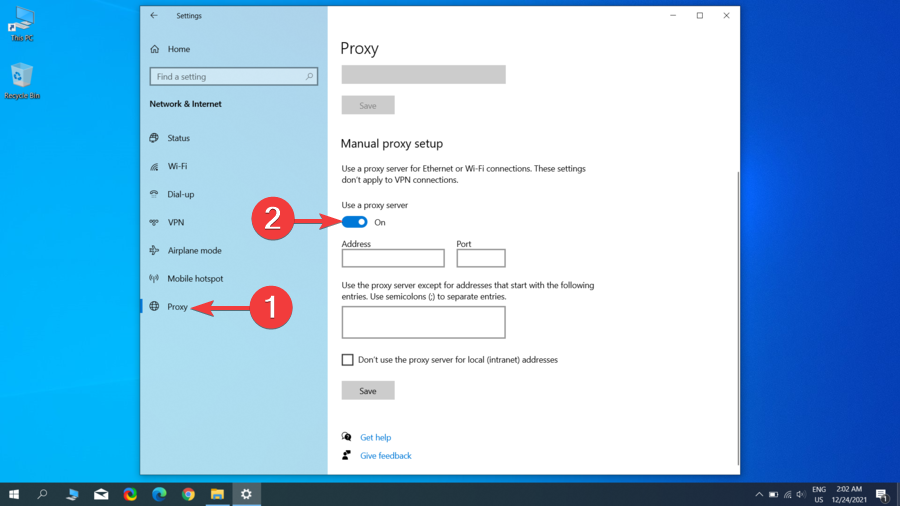
- Toggle on the Use a proxy server option.
- In the Address field, enter the proxy server name or IP address.
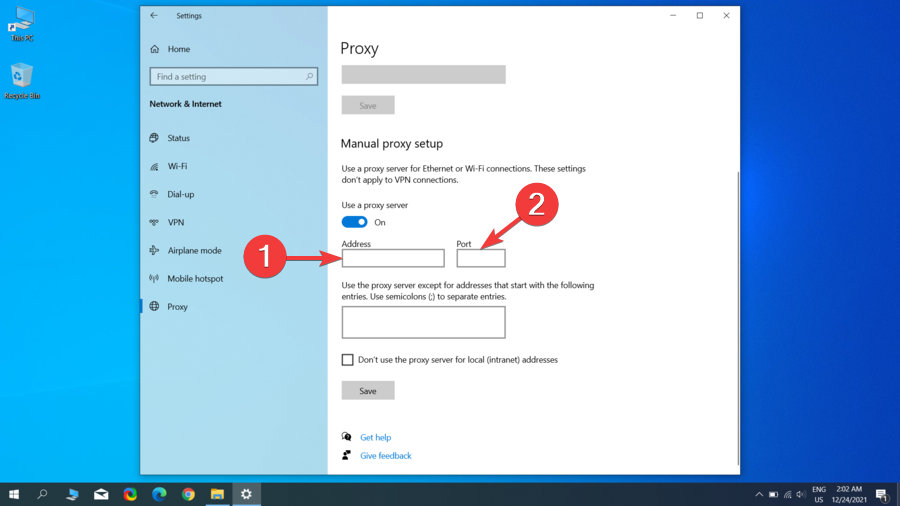
- In the Port field, enter the proxy port number, then click Save.
Firefox proxy setup
- Go to the menu and click on Settings.
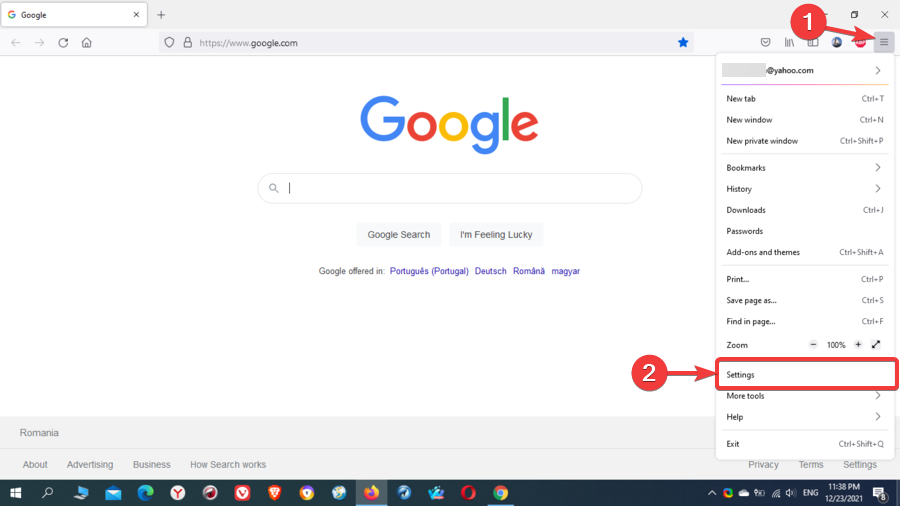
- In the General tab, scroll down to Network Settings, then click on Settings.
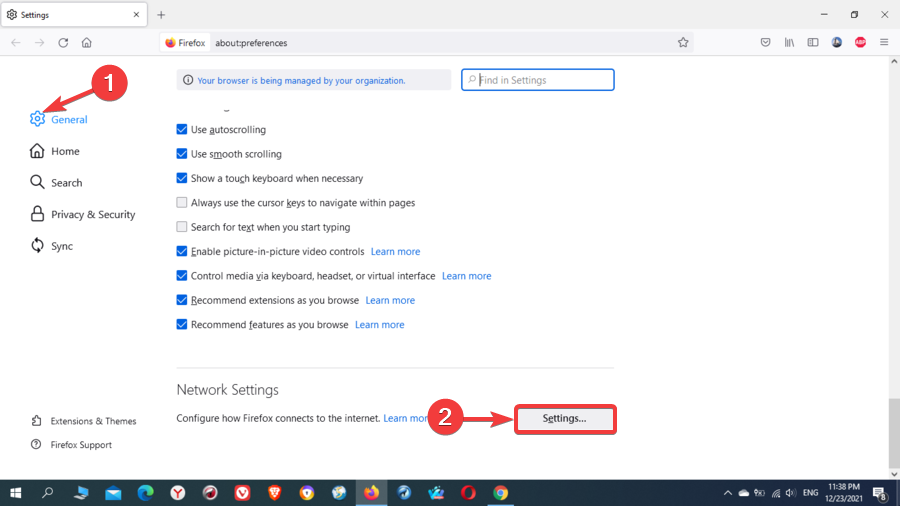
- Here, you have different options, but you can select Manual proxy configuration.
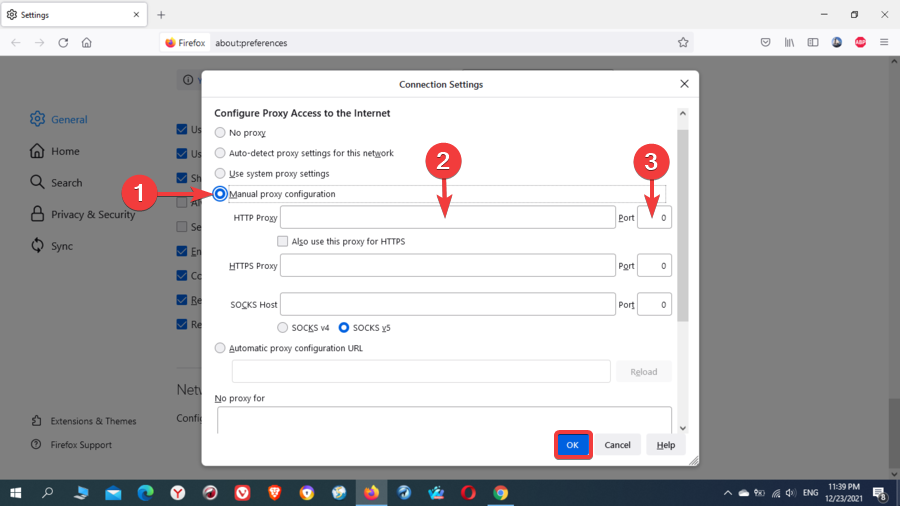
- Enter the proxy address and port number for your HTTP or SOCKS proxy, then click OK.
Which is better: VPN or proxy?
The answer to this question depends primarily on your needs and budget.
Unlocking geo-blocks
If all you care about is bypassing geo-blocking to access content not available in your current geographical area, then both a VPN and proxy server can get you around this. Thus, you may choose a proxy instead if you can’t afford a VPN.
However, it’s worth mentioning that certain websites or services, such as streaming platforms like Netflix or HBO Max can easily detect that you’re using a VPN or proxy to circumvent restrictions.
When this happens, you will be blocked from accessing any content. In this situation, a premium and reliable VPN is a far better solution than a proxy server, as it may be harder to detect.
Premium and well-reputed VPN services perfected their technology to keep up with VPN blocks, while proxies are weaker in this area since they are mostly free, have a weaker infrastructure and are also shared by many users.
If all you want is to surf the Internet anonymously, then both a VPN and a proxy server can help you achieve this since they both conceal your IP address so no one can detect your real online identity.
Protecting traffic data
However, if you want to benefit from privacy and security as well, then the only way to get them is by using a VPN. A VPN encrypts all of your traffic so no one can pry into your private online affairs.
If you wonder whether you should both a VPN and a proxy, we would have to say no. Using a VPN makes the proxy server redundant.
However, you can pair them together and switch between them depending on what you want to achieve.
Thus, you can confidently entrust it with your private sensitive data, such as conversations, passwords, and online banking credentials without worrying about cyberattacks.
Also, tracking, monitoring, or government surveillance will be a thing of the past.
A proxy, on the other hand, does not provide any form of encryption, which means that your sensitive data and activity are susceptible to breaches and surveillance while connected to a proxy server.
A VPN is the better option for those who can afford it since not only will it allow you to get around geo-blocks and censorship but it will also ensure your complete online anonymity, privacy, and security.
Please keep in mind that not each VPN works smoothly in all of the aforementioned areas.
For example, you should avoid – if possible – free services, as they come with limited features and are less reliable than premium ones both in terms of bypassing geo-blocks and also in terms of security and privacy.
Moreover, you had better choose a VPN that has a strict no-logging policy in order to maintain the highest level of privacy.
VPN providers that keep logs on users’ online activities are to be avoided because that information might end up in the wrong hands.
VPN vs Proxy – conclusion
All things considered, except for a few areas, VPNs and proxies are nothing alike. The VPN is far more complex both in terms of functionality and features provided.
Now that we’ve arrived at the end, please take into consideration the info presented in the table below so that you’ll have a general idea as to which service is more suitable for your situation.
It’s also worth mentioning that not all the features presented below can be found with any VPN service on the market. Only top premium VPNs include all or the majority of these features.
| Feature | VPN | Proxy |
| Availability | System-wide | Browser/application |
| Affordability | Premium | Free |
| Bypass geo-blocking | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Stop bandwidth throttling | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Anonymity | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Encryption | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Privacy | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Security | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Kill switch | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Split tunneling | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Multi-Hop | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Obfuscation | ✔️ | ❌ |
As you can notice, the VPN is the absolute winner. It is more reliable and can be used system-wide. Also, it guarantees full online anonymity, privacy, and security via encryption, and it also comes bundled with a host of other great features.
A proxy, on the other hand, while free or much cheaper than a VPN, can help you surf anonymously and access geo-blocked content, but unfortunately, it lacks security and privacy.
Finally, we do hope that the information presented above will help you clearly understand the differences and similarities between a VPN and a proxy server.
Now, after taking everything into consideration, it should be easier for you to decide upon which of the two is the ideal choice according to your specific needs.









User forum
0 messages