How to Fix T-Mobile Internet Not Working With VPN (Step by Step)

T-Mobile internet not working with VPN can derail remote work, streaming, and basic browsing.
The root cause is usually a mix of IPv6, carrier-grade NAT, and packet size quirks that some VPN protocols do not love. Follow these fixes in order, and test after each one.
Table of contents
- 1) Switch the VPN Protocol to TCP
- 2) Lower the MTU to Prevent Fragmentation
- 3) Force IPv4 by Adjusting APN or Disabling IPv6
- 4) Fix Hotspot-Specific Problems
- 5) iPhone Hotspot Tweaks That Help VPNs
- 6) Rebuild the VPN Profile and Try Fresh Servers
- 7) Mind Hotspot Caps That Throttle VPN Traffic
- 8) Full Checklist for T-Mobile Hotspot + VPN
- 9) When All Else Fails, Talk to Support
- Wrap-up: Make T-Mobile and VPN Play Nice
- FAQs
1) Switch the VPN Protocol to TCP
Some T-Mobile routes are unfriendly to UDP. TCP is slower on paper, but it survives stricter paths and fragmentation better. This simple swap often stabilizes work VPNs like AnyConnect, GlobalProtect, or FortiClient.
- Open your VPN app and go to Connection or Protocol settings.
- Change from UDP to TCP.
- If available, test IKEv2 and WireGuard as well.
- Save, reconnect, then try your work app or site again.
2) Lower the MTU to Prevent Fragmentation
T-Mobile’s network adds overhead. If your packets are too large, you get timeouts or partial loads. Dropping MTU to 1400 or even 1350 keeps packets intact end to end.
- In your VPN app or router, open Advanced or Network settings.
- Set MTU to 1400. If issues persist, try 1375 or 1350.
- Apply changes and reconnect the VPN.
- Load a few heavy pages or your remote desktop to confirm.
3) Force IPv4 by Adjusting APN or Disabling IPv6
T-Mobile often defaults to IPv6. Many corporate VPN stacks are still IPv4 heavy. Forcing IPv4 removes a big chunk of incompatibility.
- On Android, create a new APN and set APN protocol to IPv4.
- On Windows, open Adapter Properties and uncheck Internet Protocol Version 6.
- Reconnect mobile data or Wi-Fi, then reconnect the VPN.
- Test your company portal or cloud app.
4) Fix Hotspot-Specific Problems
If your laptop only fails when tethered, the problem may live in the hotspot path. DNS, IPv6, or sharing rules can break the tunnel while phone-only works fine. For details, see this guide on can’t connect to VPN when using mobile hotspot.
- Forget the hotspot network on the client device, then reconnect.
- Turn hotspot off and on, then reboot both devices.
- Test with 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz hotspot bands.
- Recheck VPN settings after reconnecting.
5) iPhone Hotspot Tweaks That Help VPNs
Personal Hotspot on iPhone can pass IPv6 and cause MTU pain. A few small changes often clear the runway for your VPN. See more in this guide on iPhone hotspot VPN not working.
- Turn Personal Hotspot off, then back on.
- In Settings, reset network settings, then set DNS to automatic.
- Recreate the VPN profile on the client device.
- Reconnect and test again.
6) Rebuild the VPN Profile and Try Fresh Servers
Corrupted profiles or busy endpoints can look like carrier blocks. A clean profile and a closer server can flip the result from flaky to stable.
- Delete the existing VPN profile from your device.
- Download the latest config from your provider or IT.
- Pick the nearest city or gateway and reconnect.
- If supported, enable split tunneling for work apps.
7) Mind Hotspot Caps That Throttle VPN Traffic
Hotspot plans can throttle, deprioritize, or cap traffic after a limit. That can turn a solid tunnel into molasses, especially on video calls. You can also explore options to bypass the T-Mobile hotspot limit.
- Check your plan’s hotspot allowance in your T-Mobile account.
- Test speed with and without VPN to spot throttling.
- Use Wi-Fi at home rather than hotspot when possible.
- If you must tether, manage usage carefully.
8) Full Checklist for T-Mobile Hotspot + VPN
If the failure only happens on T-Mobile hotspot, work through this combined list. A dedicated resource is available here: how to fix T-Mobile hotspot not working with VPN.
- Switch VPN to TCP, then test WireGuard or IKEv2.
- Lower MTU to 1400 on the client VPN.
- Force IPv4 on the phone or client.
- Retest after each change.
If your issues go beyond hotspot quirks and affect home service too, check this guide on how to fix T-Mobile Home Internet not working with VPN for router-level fixes and APN adjustments.
9) When All Else Fails, Talk to Support
Sometimes a line is stuck on IPv6, or a gateway firmware bug needs a nudge. A quick ticket can save hours of guesswork.
- Contact T-Mobile and ask if your line can use an IPv4-friendly APN.
- Ask your employer’s IT for profiles that support TCP and smaller MTU.
- Provide timestamps and server names so they can trace failures.
- Retest after any carrier or IT change.
Wrap-up: Make T-Mobile and VPN Play Nice
Most fixes come down to protocol, packet size, and IP version. Switch to TCP, lower MTU, and force IPv4 first. If the issue is only on hotspot, work through the hotspot-specific guides and your speeds and reliability should settle down.
FAQs
T-Mobile does not advertise blanket VPN blocks. Issues usually come from IPv6 defaults, carrier-grade NAT, and MTU fragmentation that break certain protocols or endpoints.
No. You use a third-party VPN for privacy or work access. Your employer may require a specific client like AnyConnect or GlobalProtect.
Hotspot routes and plan limits can add throttling, IPv6 quirks, and different DNS behavior. Fixes include TCP protocol, lower MTU, and IPv4 settings on the phone and client.
TCP is the safest first try. Many users also report success with WireGuard and IKEv2 after lowering MTU and forcing IPv4.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more


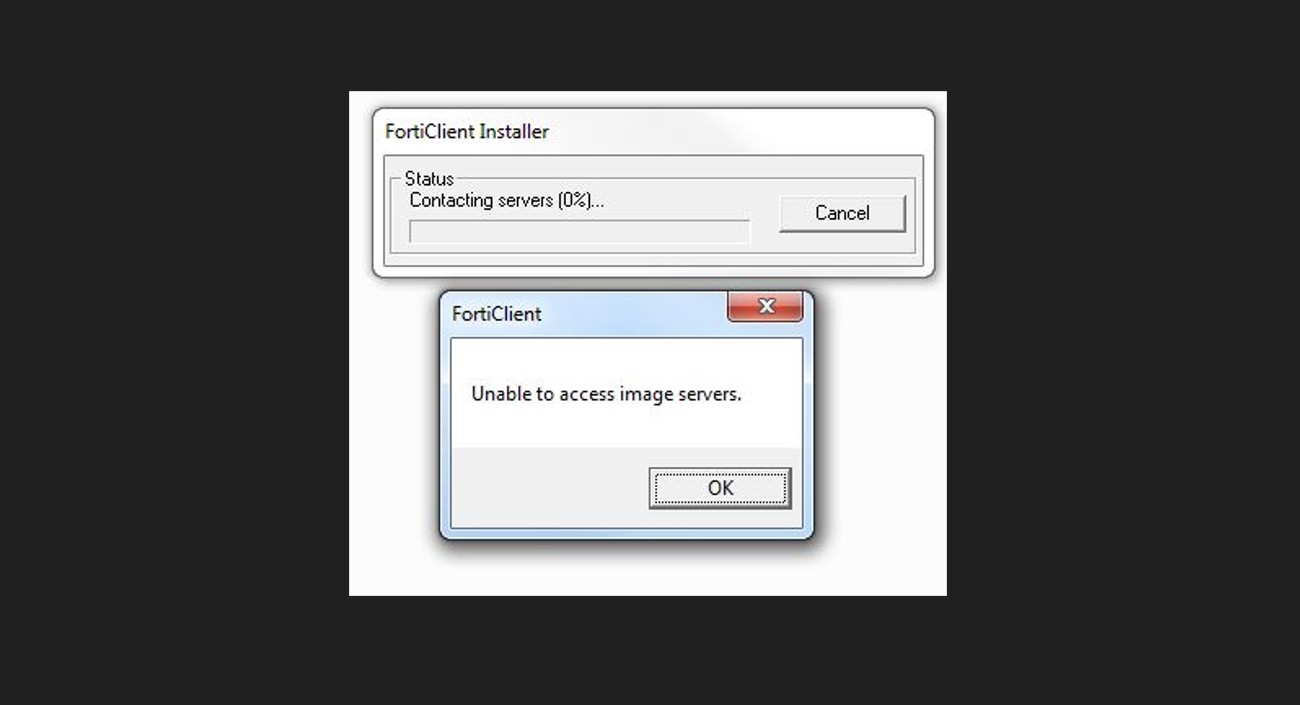


User forum
0 messages