IPv4 vs IPv6 Pros and Cons Explained [Complete Guide]
6 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more
In the complex digital landscape, two main versions of IP have emerged: IPv4 and IPv6.
While both versions have similar functions, each has its own pros and cons which set them apart.
Below, we’ll go into detail about the differences or parallels between the two.
Pros and cons of IPv4 and IPv6
Let’s break down how these two protocols work and what are the differences between them.
What are IPv4 and IPv6?
The term IP refers to Internet Protocol, a set of regulations that dictate the structure of data transmitted over the internet or local networks.
These protocols assign unique IP addresses to each device on the network, essentially acting as their digital identifier.
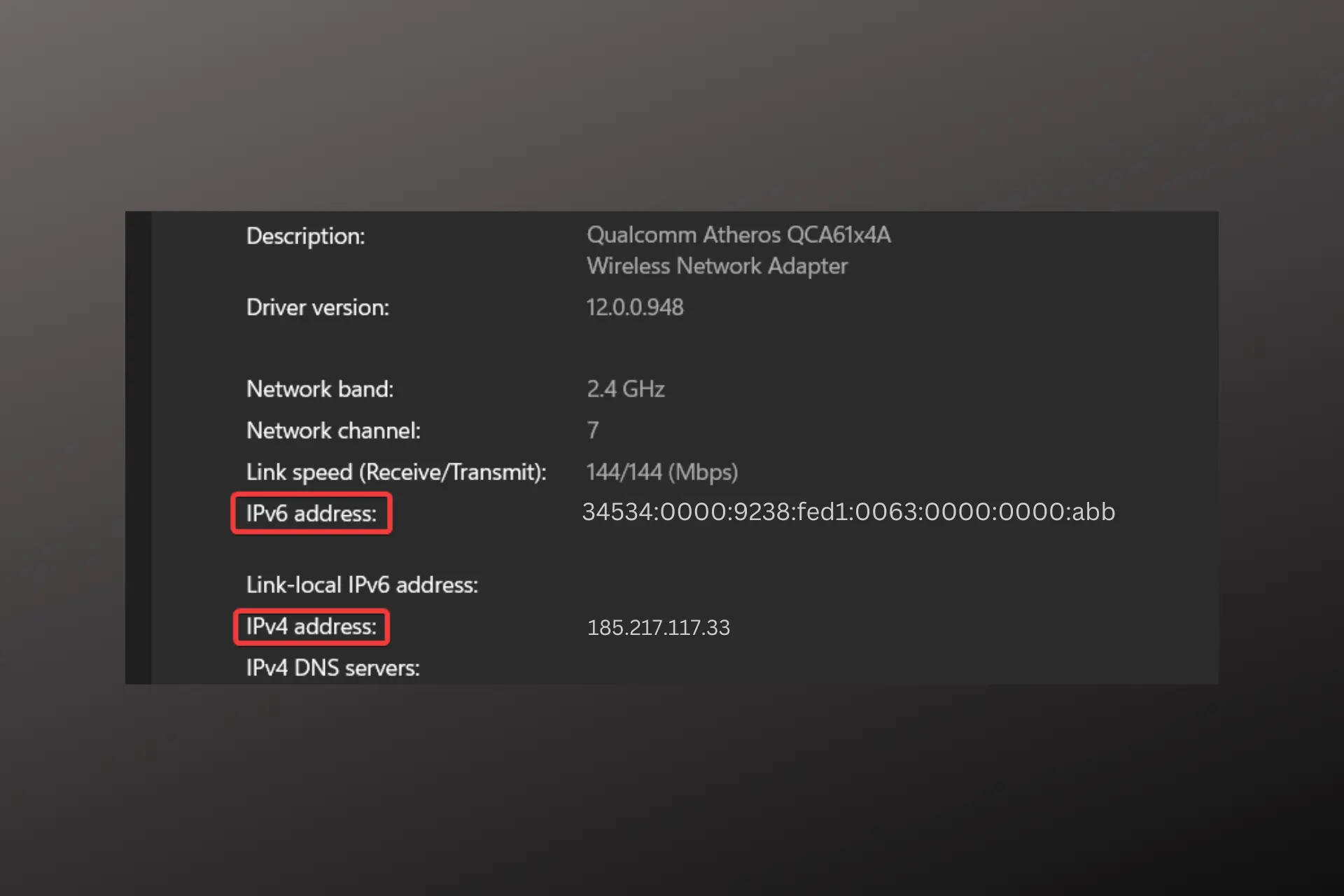
In case you’re wondering what they look like, here’s an IPv4 vs IPv6 example:
➤ IPv4 : 185.217.117.33
➤ IPv6: 3534:0000:3238:DFE1:0063:0000:0000:abba
IPv4 has been the standard for decades, but as the internet has grown, IPv4 has faced limitations regarding address space and scalability.
In response, IPv6 was developed as a more robust and efficient alternative to IPv4.
However, there are differences between the two. And knowing them will help you make an informed decision about the best for your needs.
Key differences between IPv4 and IPv6
Here’s a summary of the differences between the two and the IPv6 vs IPv4 pros and cons:
| IPV4 | IPV6 | ||
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons | ✅Pros | ❌ Cons |
| Simpler header structure | Limited address space, leading to address exhaustion | Large address space | Incompatible with some older network infrastructure |
| Widely adopted and familiar to users | Poor security features | Improved security features | Limited global deployment and adoption |
| Easier to implement | Subnetting problems | Better support for mobile devices and new devices in general | Possible system issues |
| Proven technology | 32 bits (4 bytes) | 128 bits (16 bytes) | Does not work with all VPNs |
| No auto-configuration | IP address assignment and device numbering occur automatically | ||
| Routing is made more efficient by reducing the size of routing tables |
There are some advantages of IPv6 over IPv4.
For example, IPv6 enables devices to connect to multiple networks simultaneously easily.
This results from IPv6 configurations that allow the automatic assignment of multiple IP addresses to a single device.
However, IPv4 remains widely used and well-established, making it a more suitable choice for those concerned about compatibility with existing systems and devices.
Some systems or devices may have difficulty processing and routing IPv6 traffic, leading to potential performance issues.
When deciding between IPv4 and IPv6, you should carefully consider the pros and cons of each option to determine which one best meets your specific needs.
Keeping this in mind, let’s consider which protocol is best suited for certain activities.
🎮 IPv6 vs IPv4 for gaming
IPv6 has the potential to enhance the gaming experience due to its in-built support for Quality of Service (QoS) and multicasting.
With QoS, routers can prioritize gaming traffic and reduce latency, increasing IPv6 gaming speed.
Gaming servers also perform better with IPv6, as the support for multicasting allows for more efficient data broadcasting to multiple players.
However, the full benefits of IPv6 can only be realized if all hardware, devices, and networks in the chain are using it.
Currently, many ISPs use IPv4, which often leads to IPv4 gaming latency.
So, if you’re considering the best option between IPv6 vs IPv4 for gaming, you should go for IPv6 where available.
🛡️ Network security
The IPv6 connection protocol was designed with security in mind, and when implemented properly, it is more secure than IPv4.
It includes IP Security (IPSec), a set of IETF security protocols that ensure authentication, security, and data integrity.
Also, IPv6 has improved the protocol for secure neighbor discovery (SEND), which confirms the other party’s identity during host discovery using cryptography.
It’s a security extension that ensures the network is secure.
Plus, IPv6 has a much larger address space than IPv4, making it more difficult for attackers to find a vulnerability.
With 3.4 x 1038 addresses available, it would take much more time to search for an open address than with IPv4’s 4.3 x 10^9 addresses.
Additionally, IPv6 may be a problem for VPNs, as many VPN apps only support IPv4. For that reason, some VPNs may not work when you enable IPv6.
On the other hand, you can also implement IPSec on IPv4, which means that, in theory, IPv4 has the potential to be as secure as IPv6.
However, the high cost of implementation has limited its use.
As the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 continues, the use of IPSec is expected to increase, making IPv6 even more secure in the future.
Ultimately, when it comes to comparing the security of IPv4 vs IPv6 we’ll say the latter is more secure, although it’s not implemented on a lot of networks.
⚡ IPv6 vs IPv4 speed
Theoretically, IPv6 might perform slightly better as it does not need to spend processing cycles on NAT translations.
However, IPv6 also has larger packet sizes which could result in a minor reduction in speed in certain scenarios. As a result, IPv4 may exhibit slightly better performance.
Overall, comparing the IPv4 vs IPv6 speed, the difference between the two protocols is insignificant in reality.
Why is it taking so long to switch IPv4 addresses over to IPv6?
The switch from IPv4 to IPv6 has been slow for a few reasons. One of them is the expensive and complicated process of updating network systems and devices to support IPv6.
Plus, there’s not a huge rush to switch since IPv4 is still working, there are still unused addresses, and the disadvantages of IPv4 are manageable.
And, the limited availability of IPv6-enabled devices and services is also a challenge.
But, it’s important to remember that the transition to IPv6 is happening gradually as companies consider the costs and benefits.
Conclusion
Both IPv4 and IPv6 have their pros and cons. IPv6 provides a much larger address space, advanced security features, and improved mobile devices and IoT support.
While IPv4 is widely adopted and has a simple header structure, making it easier to implement.
For optimal results, it’s advisable to maintain both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses enabled.
This is because relying solely on IPv6 can result in limited accessibility, considering only a small portion of the internet, approximately one-third, supports it.
On the other hand, turning off IPv6 can also create issues, especially if your router has already uses it.