VPS vs VPN vs Proxy: What are the Differences?

On the surface, a VPS, VPN, and proxy offer similar services. But the truth is, the three have some functional differences.
So, what are they? How do they work? Where do they stand apart? And most importantly, what are their uses?
Find all the answers in our detailed comparison below.
VPS vs VPN vs Proxy – What’s the Difference?
VPS, VPN, and proxy services have significant technical differences. Here’s a quick roundup:
- Virtual private server (VPS) – It comprises a virtual machine for hosting websites and web applications.
- Virtual private network (VPN) – This service encrypts your traffic so you can access the internet anonymously.
- Proxy – This is an intermediary server that completes web requests on your behalf.
Let’s expand on the details of the above services using the following illustration:
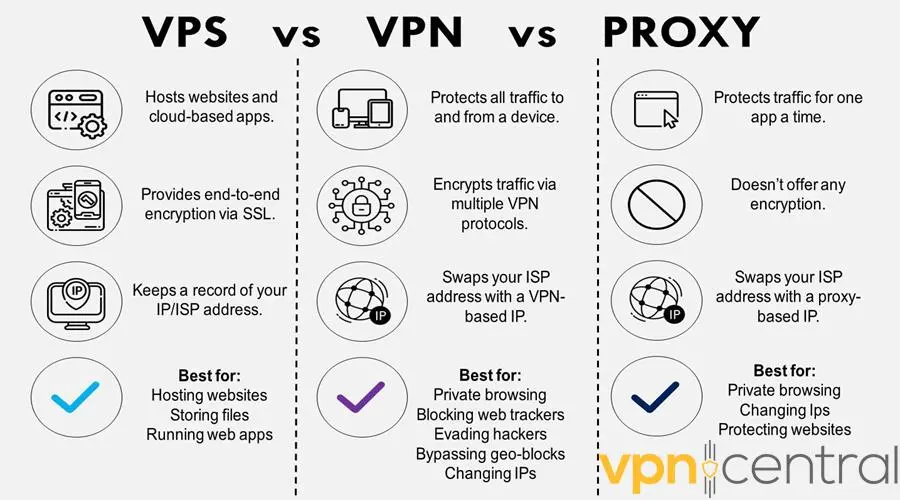
As you can see, these internet tools serve a wide range of functions. Next, we’ll examine them individually for a better understanding.
What Is a Virtual Private Server (VPS) and How Does It Work?
A virtual private server (VPS) is a virtual computer that hosts websites, files, and applications. That way, users can access the content it stores from anywhere on the planet.
The service borrows its name from the use of virtualization technology. In this case, special software is used to split a single physical machine into multiple isolated environments.
With this setup, all users benefit from dedicated resources to power applications. The outcome is reduced costs for leasing the service without compromising performance.
Other benefits include improved reliability, security, and effortless management. Besides that, you can quickly scale up your allocation of CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth.
But wait, there’s more:
A VPS is highly customizable for different use cases. This range from hosting simple websites to running demanding platforms like e-commerce.
Furthermore, a virtual server can power complex and demanding activities at scale. These include but are not limited to gaming, cloud apps, remote desktops, etc.
Web hosting providers are known to own, operate, and offer VPS services. But companies with large data requirements can have in-house setups of such systems.
What Is a Virtual Private Network (VPN) and How Does It Work?
A virtual private network (VPN) is an application that routes internet traffic through an encrypted connection to improve security and privacy.
A typical VPN service consists of strategically-located servers available in select countries worldwide. They come with unique IPs to conceal users’ real IP addresses.
VPNs rely on different protocols to guarantee top-class security. Common ones include the following:
- OpenVPN – It’s the most popular and secure VPN protocol. It encrypts traffic using SSL/TLS, making it difficult to eavesdrop.
- WireGuard – This method offers end-to-end data encoding to prevent interception by third parties. It’s also faster and more common among VPN services.
- SSTP – This VPN protocol by Microsoft uses SSL/TLS cryptography to secure communications. It also offers good speeds for internet access.
- L2TP/IPSec – Developed by Microsoft and Cisco, this protocol offers better stability, faster speeds, and superior anonymity.
Here’s where it gets interesting in this VPS vs VPN vs Proxy comparison:
Using a virtual private network is pretty simple. All you need to do is choose an ideal server country and connect.
Once you do that, the VPN switches your ISP’s address with that of the location you selected. This way, you’ll be able to bypass geo-blocks, censorships, and ISP restrictions.
However, unlike VPSs, VPNs only offer bandwidth for internet usage. As such, no other tasks are necessary, like customizing a server before using it.
What Is a Proxy and How Does It Work?
A proxy is a computer that fulfills internet requests on your behalf. It redirects traffic through a remote server before using the same gateway to deliver content back to you.
This channel works similarly to a VPN. For instance, it spoofs your ISP address with an IP that belongs to a different geo-location.
So, it’s effective for evading internet censorship by virtually switching your location. Moreover, you can use it to browse the internet privately.
On the downside, a proxy doesn’t encrypt your traffic like a VPN. As a result, a middleman can easily intercept your connection and steal your data.
But this is where it stands apart:
Web developers rely on proxy servers to serve multiple complex tasks. They can configure it to deliver websites and cloud apps with speed.
Proxies also filter visitor traffic by targeting IPs to block spammers. When anti-bot protections trigger, you may see a related symptom such as a proxy error with no response from bot. Furthermore, they help prevent hackers from compromising cloud-hosted applications.
All in all, there are three main types of proxy servers. They include the following:
- Anonymous proxy – It shields traffic behind an internet gateway to safeguard your privacy. It’s ideal for browsing the web in incognito.
- Forward proxy – It filters incoming website traffic to block unwanted visitors.
- Reverse proxy – It helps speed up websites and cloud apps by balancing traffic across multiple web servers.
Now to the ultimate question.
VPS vs VPN vs Proxy – Which One Is Better?
In summary, a VPS, VPN, and proxy share similar traits. But they work differently and serve diverse needs.
Get a proxy server if you need to casually browse the web and unlock geo-locked content. It provides basic privacy and lets you virtually change your location on the fly.
However, a VPN is a better option if your security is at stake. It’s easy to use and offers a wide variety of server regions to hide your traffic.
But if you want to set up a business online, go for a VPS. It’s ideal for hosting files, websites, and web applications.
Overall, this VPS vs VPN vs proxy comparison is done and dusted. It’s now your turn to pick the right option for your needs. For another perspective on how VPNs compare with other networking technologies, check out our full guide on VPN vs VLAN.
For readers exploring more cloud-based alternatives, we also have a full breakdown of VPN vs VPC that highlights how private networks compare with virtual private clouds.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more






User forum
0 messages