VPN Tunnel Types — How They Work and Best Use Cases

Some of the biggest challenges Internet users face today are online security and privacy.
With the increase in the transmission of sensitive information over the Internet, the attempts to steal such data do also increase.
And that’s where VPNs come in.
One VPN’s key components are the VPN tunnel, which is responsible for encrypting and transmitting data over the Internet.
Today, there are lots of VPN tunnel types available. But they all have different performance levels.
So, we’ll look at VPN tunnel types and other valuable information about them.
VPN tunnel types at a glance
There are several VPN tunnel types, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
To help you understand the options available, we’ve created a table that compares the most common VPN tunnel types based on their encryption, speed, and security.
Here’s it.
| Tunnel Type | ? Encryption | ⚡ Speed | ?️ Security |
| PPTP | 128-bit | Fast | Weak |
| L2TP/IPSec | 256-bit | Moderate | Moderate |
| SSTP | 256-bit | Fast | Strong |
| OpenVPN | 256-bit | Moderate | Strong |
| IKEv2 | 256-bit | Fast | Strong |
| WireGuard | ChaCha20 | Fast | Strong |
What is a VPN tunnel?
A VPN tunnel is a secure, encrypted connection between two or more devices that transmit data over the Internet.
The main benefit of using a VPN tunnel is improved online privacy and security.
This encryption ensures your data transmitted remains confidential and untampered, as no one can monitor your online requests.
Additionally, by routing your traffic through a VPN server in another part of the world, VPN tunnels can help bypass Internet censorship and access restricted content in your location.
While VPNs tunnels have their benefits, they also have their limitations.
For example, because tunneling uses packets and encryption through an Internet connection, VPN tunneling is often slower than typical network connections.
Also, many companies are combating VPN tunneling use by implementing VPN blockers on their websites to restrict access.
These programs track the IP addresses of registered users and block access if they can trace it back to a VPN or proxy. However, there are VPN services that use up-to-date privacy features that can get past that block.
How do VPN tunnels work?
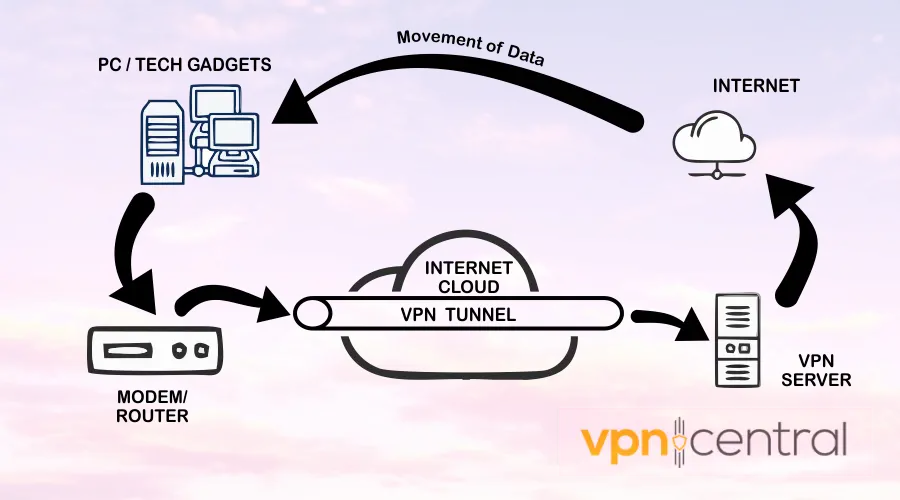
There are 2 major types of VPN connections: tunneling and bridging. Basically, VPN tunneling is using a commercial VPN service.
So, the answer to “How does VPN tunneling work?” is the same as “How does a VPN service work?”
When you connect to a VPN, your traffic is routed through the VPN server, which acts as an intermediary between your device and the Internet.
This means you send your requests to the web via tunneling.
The VPN server encrypts your data before transmitting it over the Internet, ensuring that your online activity remains private and secure.
Additionally, the VPN tunnel divides your information into smaller units called “packets” and then encapsulates them within other data packets.
This encapsulation process enhances the security of your data and protects you from potential attacks.
VPNs use a cryptographic key to encrypt all data transmitted through it, ensuring that neither hackers, trackers nor your Internet Service Provider (ISP) can access it.
VPN tunnel types – explained
There are several VPN tunnel types, each with its own strength.
Let’s take a closer look at the most popular VPN tunnel types and when you should use each.
PPTP – good speed, but outdated security
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) is known for its speed and ease of use. However, it is also one of the weakest VPN tunnel types in terms of security, as it uses 128-bit encryption.
PPTP has a long history, being one of the first protocols to enter the world of VPNs. It dates back to the era of Windows 95.
Since it has been around for a while, its reliance on the obsolete MS-CHAP v2 authentication suite makes it susceptible to hacking.
However, this vulnerability provides a trade-off. Due to its encryption type, PPTP is the fastest VPN protocol available.
While this allows for fast connections, it also means that your data is less secure. 128-bit encryption algorithms are becoming more and more vulnerable as new threats emerge.
When should you use PPTP?
PPTP is best used for low-security activities, such as browsing the web on pages you know for a fact are completely harmless, or accessing non-sensitive information.
However, it is not recommended for applications that require strong security, such as online banking or storing sensitive information.
L2TP/IPSec – up-to-date encryption with moderate speed
L2TP/IPSec (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol/Internet Protocol Security) is a more secure VPN tunnel type than PPTP, as it uses 256-bit encryption.
L2TP is a protocol developed as an improvement to L2F and PPTP. It was first introduced in 1999 and is often used with IPsec for better security.
IPsec provides end-to-end encryption and authentication by encrypting and verifying each IP packet in a communication.
When combined, L2TP and IPsec offer stronger protection than PPTP, but they are primarily intended for anonymization rather than security.
Also, L2TP can sometimes experience difficulties with firewalls due to UDP port 500, which some firewalls block.
Nevertheless, L2TP and IPsec offer a more secure option for VPN users than PPTP alone.
When should you use L2TP/IPSec?
It may be the best choice for applications requiring moderate speed and good security as it is slightly slower than other VPN tunnel types.
SSTP – good encryption and speed, easy to detect
Just like L2TP/IPSec, SSTP or Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol offers better security than PPTP, because it uses 256-bit encryption.
It also uses features that make it easier for SSTP to bypass firewalls blocking certain ports, providing enhanced user security.
These include SSL/TLS for secure key negotiations and TCP port 443 for encrypted transfers.
However, one potential drawback of SSTP is that it relies on user authentication rather than device or computer authentication, which could limit its usage in certain circumstances
When should you use SSTP?
In theory, SSTP can be used for applications that require both speed and security, such as streaming and secure browsing.
However, it’s slowly becoming outdated and lacks a few modern privacy features. ISPs and services that block VPNs don’t typically have a hard time detecting and banning SSTP tunnels.
OpenVPN – up-to-standard and versatile protocol
OpenVPN is a widely used VPN tunnel type known for its flexibility and robust security. It uses 256-bit encryption and is relatively fast, making it a good choice for many applications.
Although it may require a bit more setup than other protocols, OpenVPN provides exceptional speed, security, and encryption.
Users can choose between UDP, optimized for speed, or TCP for connection reliability, offering a customizable experience.
When should you use OpenVPN?
OpenVPN is a versatile VPN tunnel type suitable for many applications, from low-security browsing to high-security like online banking.
It meets current security requirements and is compatible with a lot of different devices.
IKEv2 – stable and fast but has some vulnerabilities
The IKEv2 protocol (Internet Key Exchange version 2) uses 256-bit encryption, making it a good choice for security.
It is a relatively recent VPN protocol designed to be a lightweight and reliable version of OpenVPN.
Its efficiency and stability make it an ideal choice for those using mobile devices across various platforms.
However, it should be noted that IKEv2 operates exclusively through UDP, which some firewalls may restrict.
When should you use IKEv2?
Using IKEv2 is a good idea if you want to browse the web securely, without much worry that your connection will fluctuate or drop. Because it’s using only UDP, we’d say it’s not as secure as other options.
It’s not the best protocol for speed, but it can still work ok for streaming and gaming.
WireGuard -fast, stable, and secure
WireGuard is a relatively new VPN tunnel known for its speed and simplicity.
It uses ChaCha20 encryption which is typically considered just as secure as AES/GCM or even better.
WireGuard® boasts a lightning-fast performance due to its cutting-edge cryptographic technology and seamless integration with the operating system kernel.
Also, many users claim it provides faster speeds compared to OpenVPN.
Additionally, WireGuard uses the UDP protocol and offers flexible port configuration options.
However, it may be more susceptible to detection and throttling than OpenVPN, as it doesn’t support TCP.
When should you use WireGuard?
You can trust WireGuard for applications that demand strong security, such as accessing sensitive information or financial accounts.
Summary
VPN tunnels are a crucial component of VPN technology, responsible for encrypting and transmitting data over the internet.
Several VPN tunnel types are available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. To make the best choice for your needs, consider factors such as encryption, speed, and security.
Whether you’re looking to protect your online privacy, access restricted content, or simply enjoy faster, more secure internet access, a VPN tunnel can help you achieve your goals.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more





User forum
0 messages