11 Best Residential Proxies [For Beginners & Professionals]
Unlock the internet's potential with these top-notch residential proxies
16 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more

Are you looking for the best residential proxies? Today is your lucky day.
I’ve tested and used 50+ vendors over the last five years. And I know how tiresome it is to find the right one.
Luckily, I’ve rounded up the top 10 providers right now. That way, I can spare you all that trouble for things that matter.
Let’s check them out.
The best residential proxies
Check the top residential proxies vendors on the market below.
- Decodo – Best overall
- Oxylabs – Best for developers
- Webshare – Best for budget-friendly proxies
- IPRoyal – Best for sticky proxy sessions
- Froxy – Best private residential proxies
- ScrapingBee – Best for scraping
- Bright Data – Best for market research
- ASocks – Best for beginners
- LunaProxy – Best value for money
- 922Proxy – Best for unlimited traffic
- DataImpulse – Best for small business
Here’s a side-by-side comparison:
| User Tools | Proxy IP Pool/Countries | Response Rate/ Success Rate | Concurrent Connections | Security/ Encryption | Free Trial/ Pricing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Decodo | – Web app – X Browser – API | – 55+ million/ – 195+ countries | – 0.3 seconds/ – 99.99% | – Unlimited | – HTTPS – SOCKS5 | free trial/ – From $1.5/GB |
| 2. Oxylabs | – Web app – Endpoint generator – API | – 100+ million/ – 190+ countries | – 0.6 seconds/ – 99.95% | – Unlimited | – HTTPS – SOCKS5 | Free trial/ – From $10/50GB |
| 3. Webshare | – Web app – API | – 30+ million/ – 195+ countries | – 0.7 seconds/ – 99.80% | – Unlimited | – HTTPS – SOCKS5 | – Free trial/ – From $7/GB |
| 4. IPRoyal | – Web app – API | – Over 2 million/ – 190+ countries | – 5.2 seconds/ – 99.70% | – Unlimited | – HTTPS – SOCKS5 | – No trial/ – From $7/GB |
| 5. Froxy | – Web app – API | – Over 8 million/ – 200+ countries | – 0.8 seconds/ – 99.94% | -1,000 | – HTTPS – SOCKS5 | – $1.99 paid trial/ – From $7/GB |
| 6. ScrapingBee | – Web app – API | – Undisclosed/ – 200+ countries | – 0.5 seconds/ – 98.50% | – From 5+ | – HTTPS – SOCKS5 | – 1,000 free credits/ – From $49/month |
| 7. Bright Data | – Web app – Web unblocker – Proxy manager – Google Chrome extension – API | – 350+ million/ – 195+ countries | – 0.5 seconds/ – 99.95% | – Unlimited | – HTTPS – SOCKS5 | – Free trial/ – From $5.88/GB |
| 8. ASocks | – Web app – API | – Over 7 million/ – 150+ countries | – 0.9 seconds/ – 99.78% | – Unlimited | – HTTPS – SOCKS5 | – Free trial/ – From $3/GB |
| 9. LunaProxy | – Web app – Desktop proxy manager – API | – 200+ million/ – 195+ countries | – 0.6 seconds/ – 99.9% | – Unlimited | – HTTPS – SOCKS5 | – No trial/ – From $0.7/GB |
| 10. 922Proxy | – Web app – Desktop proxy manager – API | – 200+ million/ – 190+ countries | – 0.8 seconds/ – 99.97% | – Unlimited | – HTTPS – SOCKS5 | – Free trial/ – From $3/GB |
| 11. DataImpulse | – Web app – API | – Over 5 million/ – 190+ countries | – 0.9 seconds/ – 95.6% | – Unlimited | – HTTPS – SOCKS5 | – Free trial/ – From $1/GB |
1. Decodo (formerly Smartproxy)
Decodo stands out as a reliable and affordable provider of residential proxies. Its network comprises 55+ million residential-based IPs in 195+ locations.
This vendor’s proxies come from clean sources attached to real user devices. As such, you’ll experience fast speeds, with connectivity averaging 0.6 seconds.
You get automatic rotation of IPs out of the box. This is crucial to evade CAPTCHAs and IP bans on sites you scrape.
Connections are secure, featuring HTTPS and SOCKS5 protocols. This not only boosts trust online but also enhances your privacy.
Another plus is the X Browser, which is useful for creating unique browser profiles. It supports sticky/rotating IPs, geo-targeting, fingerprinting, and more.
Other extras include exceptional 24/7 customer support and well-detailed documentation. Above all, you can enjoy this service for $1.5/GB.
You can use the code RESI50 to get 50% off (this is a limited-time offer).
✅ Pros:
- 99.45% success rate
- Unlimited connections
- Multiuser X browser
- Supports encryption
- Volume-based pricing
❌ Cons:
- Registration requires ID verification

Decodo
Benefit from a huge pool of residential IP addresses and advanced features with Decodo.2. Oxylabs
Oxylabs is a well-known premier proxy vendor. The company boasts over 100 million residential IPs spanning 190+ countries.
Connection speeds average 0.6 seconds, backed by an outstanding 99.90% uptime. Moreover, Oxylabs’ proxies fulfill requests with a success rate above 99.95%.
Like Smartproxy, it supports automatic rotation of IPs by default. Time-based sticky sessions also allow you to route requests through the same IPs.
There’s geo-targeting to gather data from specific countries, cities, and zip codes. Even better, targeting internet service providers (ASNs) is equally possible.
The endpoint generator is another thing to appreciate about Oxylabs. It’s developer-friendly and supports coding languages like PHP, Node.js, Java, etc.
Customer support is available around the clock via chat. Besides that, the $8/GB makes it ideal for beginners and professionals.
✅ Pros:
- Easy to use
- Unlimited connections
- HTTP/HTTPS/SOCKS5 support
- 30-minute sticky sessions
- CAPTCHA/IP block avoidance
❌ Cons:
- Steep learning curve
- No crypto payments

Oxylabs
Access 100M+ residential IPs with top-tier performance and reliability3. Webshare
Webshare is a budget-friendly proxy provider offering a mix of residential, ISP, and datacenter proxies. Its network spans 30+ million IPs across 50+ global locations.
Performance is solid, with response times averaging under a second. Users can choose between rotating and sticky IPs, ensuring flexibility for web scraping, automation, and data gathering.
Security is a priority, featuring HTTPS and SOCKS5 support for encrypted connections. Plus, the user-friendly dashboard makes managing proxies effortless—even for beginners.
Webshare also stands out with its free proxy plan, allowing users to test the service before committing (you only need to make an account). Paid residential plans start from just $7/GB.
✅ Pros:
- Free datacenter plan available
- Fast response times
- Supports HTTP, HTTPS & SOCKS5
- Simple and intuitive dashboard
- Ethically-sourced premium residential network
❌ Cons:
- Limited support options (AI chatbot and email only)

Webshare
Get fast, affordable, and reliable proxies for your web scraping and automation needs.4. IPRoyal
If monthly renewal plans are not your cup of tea, get IProyal. It offers non-expiry subscriptions from as low as $7/GB.
Pricing aside, this vendor has 2+ million residential proxies in 195 countries. Like competitors, it sources them from ethical sources that are spam-free.
Scaling up your projects is easy, thanks to unlimited concurrent connections. Additionally, automatic rotation of IPs ensures CAPTCHAs and IP bans won’t slow you down.
What I like about it is the seven-day sticky proxy sessions. With this, you can use the service for web browsing, like a VPN.
You can scrape data from any country, state, and city around the world. But zip code and ASN targeting aren’t available at this time.
A tester is available to check the quality of proxies beforehand. Once satisfied, you can compile a list and export it in TXT format.
✅ Pros:
- Privacy-friendly IPs
- HTTP, HTTPS, SOCKS5 proxies
- Non-expiry traffic
- Auto-IP rotation
- Instant IP changes
❌ Cons:
- Blocks access to some services
- Bans account without warning
- Average customer support
- Steep learning curve
- Dodgy refund policy
5. Froxy
Froxy prides itself on being a trusted and cost-effective provider of private residential proxies. These are unique to every user – perfect for safeguarding your privacy.
The vendor’s network comprises 8+ million IPs available in over 200 countries. Scraping data gives you broad access to regions, cities, and ASNs.
Unfortunately, Froxy supports only up to 1,000 concurrent connections for every IP. However, this limitation boosts the efficiency of delivering results.
The good news is this service supports a wide range of integrations. They include the scrapers, proxy managers, sneaker bots, etc.
The user dashboard also makes Froxy a perfect choice for beginners. It’s clean and easy on the eye, with every tool you need just a click away.
Apart from that, technical support is available day and night. But, the agents sometimes take time to fix issues.
✅ Pros:
- User-friendly
- Excellent 99.99% uptime
- HTTP, HTTPS, SOCKS5 proxies
- Crypto payments supported
- 24/7 technical support
❌ Cons:
- $1.99 paid trial
- No refunds for paid trials
- Expensive plans
- Slow support
- Basic user documentation
6. ScrapingBee
When it comes to scraping, the ScrapingBee takes the crown. Choosing this vendor gives you access to user-friendly tools that will make your job effortless.
First, you get an intuitive dashboard where all the action takes place. It’s well laid out, with everything you need within reach.
You can go from scraping a simple URL to extracting a website’s HTML code. Moreover, I found the ability to screenshot and download a site’s images fascinating.
There’s a preview option to glimpse what the output would look like. This gives you room to fine-tune your proxies for better results.
I didn’t encounter any issues arising from CAPTCHAs and IP blocks. So scaling your projects would hardly be a problem using this service.
With all that aside, the $49/month starting price is pretty steep. Even worse, you need to part with $599/month for 200+ concurrent connections.
✅ Pros:
- Ad blocker
- JavaScript rendering
- Geo-targeting
- Detailed user documentation
- Fast customer support
❌ Cons:
- Expensive
- Usage-based pricing
- Average speeds
- Lacks city/zip code targeting
- Concurrent connection limits
7. Bright Data
Bright Data positions itself as an enterprise-grade residential proxy vendor. Its massive network dwarfs Oxylabs, featuring 350+ million IPs across 195 countries.
Such an expansive geographical reach provides seamless access to websites worldwide. Moreover, its AI-powered web unblocker makes bypassing geo-restrictions a breeze.
Bright Data’s proxy response time is also exceptional, averaging 0.5 seconds. A flawless 100% uptime guarantee ensures seamless connectivity for non-stop data retrieval.
You can make good use of the robust scraping browser to turbocharge projects. It’s developer-friendly and supports proxy rotation, fingerprinting, and automation.
The vendor additionally provides an API for conducting market research. Alternatively, you can use readily available datasets obtained from scraping ecommerce platforms like Amazon.
Another you’ll like is the proxy manager for organizing your residential proxies in one place. Here, you’ve full control for white/blacklisting IPs, set geo-targeting, auto-configuring rules, etc.
✅ Pros:
- City, zip code, ASN targeting
- SOCKS5 support
- Dedicated IPs
- Rotating/sticky proxies
- Google Chrome extension
❌ Cons:
- Steep learning curve
- Slow customer support
- Registration requires ID verification
- Bans users without warning
- Questionable privacy policy
8. ASocks
ASocks is a lesser-known provider of residential proxies. But its simplicity will draw your attention if you’re a newbie.
Unlike bigger rivals, this provider’s user dashboard is the most basic yet. All you get is a simple proxy generator for your convenience.
Supported services include geo-targeting based on countries, states, and cities. Another surprise is ASN targeting, which some popular providers lack.
There’s traffic monitoring to help you track your traffic usage. But you don’t have to worry, considering pricing starts from $3/GB.
ASocks offers slightly above seven million proxies in 150+ countries. As usual, these come from clean sources to avoid CAPTCHAs and IP bans.
On the downside, customer support is available through the Telegram app. The knowledge base also needs more documentation to improve ease of use.
✅ Pros:
- Easy to configure
- Dark mode support
- Unlimited concurrent connections
- Traffic monitoring
- 24/7 customer support
❌ Cons:
- 10-minute response time
- Dodgy free trial
- Inconsistent connectivity
- Lacks advanced tools
- Slow technical support
9. LunaProxy
LunaProxy breaks the jinx that residential proxies are expensive. Its pricing plans start from as little as $0.7/GB/month.
You can even extend the expiration date for your subscription at a discount. Plus, you stand to get a 200GB sign-up bonus.
LunaProxy doesn’t slack when it comes to quantity and quality. The vendor’s network comprises 200+ million proxies in 195 countries.
You do get access to all IPs despite the service being dirt cheap. It supports unlimited connections with a high 99.9% success rate.
There’s a beginner-friendly dashboard to manage your proxies. Or else, go with the desktop application, which I found lightweight and easy to use.
Before I forget, LunaProxy offers residential proxies with unlimited traffic for heavy users. But it will set you back a whopping $76/day.
✅ Pros:
- Cheap
- Unlimited traffic
- HTTP, HTTPS, SOCKS5
- Pay-as-you-go (PAYG) option
- Large IP pool
❌ Cons:
- No trial
- Slow residential proxies
- Inconsistent connectivity
- Barebones documentation
- Terrible customer support
10. 922S5Proxy
922S5Proxy also joins the bandwagon of cheap residential proxy providers. The pricing starts from $3/GB, which comes bundled with unlimited connections.
Its proxy pool comprises 200+ million IPs available in 190+ countries. These are fast, stable, and secure, suitable for running tasks uninterrupted.
Like LunaProxy, a robust desktop proxy manager is available for major operating systems. I loved that I could drag and drop programs into it to proxy traffic.
Geo-targeting covers the usual country, city, and state parameters. 922S5Proxy also makes it easy to target ASNs based on service provider names.
SOCKS5 and HTTPS are available onboard to maximize privacy. However, the unencrypted HTTP connection gave me the fastest response time.
An AI-powered chatbot handles live chat support decently. But you’ll need to open a ticket if you encounter technical issues.
✅ Pros:
- Affordable
- Large IP pool
- Supports crypto payments
- Well-detailed documentation
- Windows, Mac OS, and Linux apps
❌ Cons:
- No-free trial
- IP-based pricing
- Slow customer support
- Unstable sometimes
- Confusing brand names
11. DataImpulse

DataImpulse is another good alternative to IPRoyal for users who prefer non-expiry subscriptions. Its PAYG services start from $1/GB and include access to 5+ million IPs.
Geographical coverage includes roughly 140+ top-tier countries. While it can’t match bigger players, it’s decent for lightweight tasks.
DataImpulse employs a Chromium-based browser for real user-like web page rendering. Combined with flexible proxy rotation, you’re assured of evading CAPTCHAS and IP blocks.
Securing proxies is hassle-free using a username/password combination. You can also whitelist your device IPs to lock out bad guys.
Scaling tasks won’t be an issue using its simple API integration. All it takes is just a single line of code to get the job done.
You have the choice of using email to seek help. But you will rarely need it, given the vendor’s well-detailed user documentation.
✅ Pros:
- Affordable
- Easy to use
- SOCKS5 residential proxies
- Auto-rotate/sticky sessions
- 24/7 support
❌ Cons:
- No trial
- Unsuitable for high-traffic tasks
- Limited customization options
If you’ve reached this far, I’m sure you might be asking…
How do residential proxies work?
Residential proxies are proxy servers that use IP addresses assigned to real households. They’re normally attached to devices like smartphones, computers, routers, etc.
This often makes them appear like legitimate internet users. Such an approach is vital for bypassing geo-restrictions, avoiding CAPTCHAs, and maximizing privacy.
So, here’s how that works:
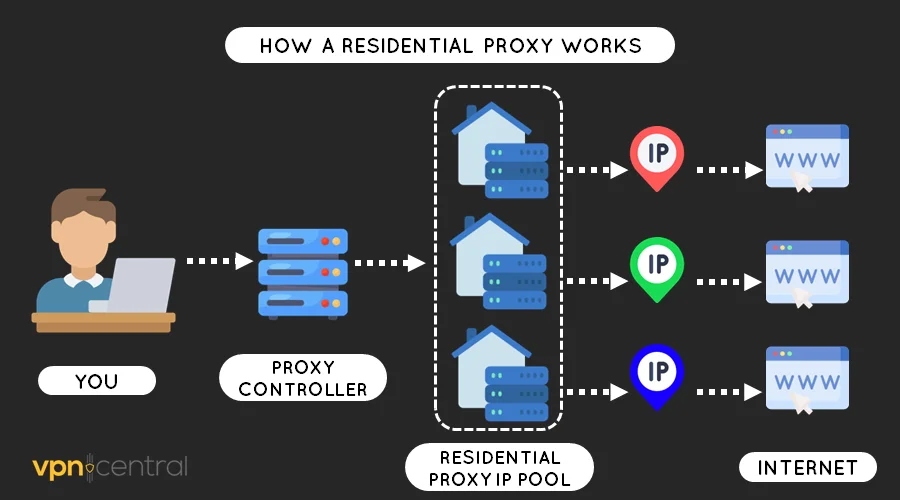
When you connect to a residential proxy, your requests go through a proxy controller. It comprises software that assigns your queries unique IPs from an IP pool.
The speed and security of your traffic depend on the chosen protocol. HTTPS and SOCKS5 are more secure, but the insecure HTTP is faster.
Residential proxies defer from other proxy types like ISP, mobile, and datacenter. But they work in an almost similar fashion.
ISP proxies, as the acronym suggests, come from internet service providers. These are usually hosted in data centers but aren’t assigned to user devices.
In terms of cost, ISP proxies are fairly affordable. You’ll find them fast, reliable, and secure.
As for mobile, these are a special type of residential proxy. However, they bear IPs originating from 3G/4G/5G cellphone carriers.
You can imagine them as the top of the cream for proxy services. They have superior security, privacy, and trust on the web, but are more expensive.
On the other hand, data center proxies aren’t usually associated with any ISPs and devices. They’re virtually generated and housed in large data centers.
This makes them cheaper than any proxy service out there. But their lack of association with any ISP causes them to get flagged more often.
Now, let’s move to another interesting topic:
Benefits and use cases for residential proxies
Residential proxies offer several benefits and have a range of use cases. They come in handy for activities where authenticity and non-detection are key.
The advantages include:
- High anonymity: Residential proxies hide your device behind a pool of legitimate IP addresses. This makes it challenging for online platforms to track your activities and location.
- Legitimacy in geo-specific access: These proxies can access geo-restricted content by providing an IP address from a specific location. You’ll find this useful for testing geo-specific advertisements or content.
- Reduced risk of blacklisting: Their legitimacy means a lower risk of being blacklisted by websites. As mentioned earlier, they appear as regular users rather than proxies.
- Versatility in web scraping: Residential proxies are the real deal for data collection and web scraping. They can access and extract data on websites without triggering anti-scraping measures.
There are quite some cases where residential proxies flourish. The following are the ones that stand out:
Ad verification
Residential proxies are invaluable for ad verification. Companies utilize them to anonymously verify their ads across different regions.
Doing so ensures the advertisements appear to the target audience as intended. Moreover, you can double-check fraud, unauthorized placements, and competitors’ malicious activities.
ScrapingBee does an amazing job here of taking screenshots of web pages with ads. I also like how it can preview results before deploying your proxies.
Market research
Residential proxies enable access to online services from a local user’s perspective. This is crucial for gathering accurate data on regional trends, consumer preferences, and competitive landscapes.
Your analysis will let you optimize marketing strategies to boost low-performing territories. Accordingly, you can increase revenues without digging deeper into your pockets.
Residential proxies are also helpful in tracking your competitors. You can check their product offerings and devise a game plan to outsmart them.
Bright Data shines here with its proprietary web scraping SEO monitoring API. It even provides pre-scraped datasets for popular platforms to get you started fast.
SEO monitoring
If you’re into SEO, then residential proxies are a must-have. They’re useful for analyzing search engine results from multiple geographical locations.
That way, you get to understand how your website compares against rivals. This can help optimize your site to rank better across different regions.
All residential proxy providers can perfectly do the job. But go with providers with a large IP pool for better geographical reach.
Social media management
Running multiple social media profiles can sometimes be troublesome. It can trigger the security systems of such platforms to restrict your activities.
However, residential proxies allow you to run accounts from different IP addresses. Doing it this way reduces the risk of raising eyebrows and attracting suspensions.
Decodo shines here with its multiuser X Browser. To avoid detection, you can add multiple user accounts with unique fingerprints.
Ecommerce operations
Ecommerce sites frequently change prices based on location or competitor pricing. Residential proxies enable businesses to monitor such behaviors, letting you perform competitive price analysis.
They also assist in checking the availability of products and services across regions. This ensures consistency and helps to enhance customer experience.
Decodo, Bright Data, and Oxylabs work for ecommerce tasks. Their fast response time will enable you to collect the desired data quickly.
Summary
I hope this list of the best residential proxies helps you find a reliable provider. If you’re still unsure, revisit the comparison table for valuable insights.
Or you can pick a different approach. Take advantage of the free trials and evaluate the services yourself.
It also won’t hurt to check out the top scraper proxy vendors. That way, you’ll be able to find a service that surely matches your needs.









User forum
0 messages