VPN vs Forward Proxy - Which One Should You Use and When?
9 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more
VPNs and proxy servers are both excellent choices when it comes to accessing geo-restricted content.
Not only that, they both protect the user’s privacy while browsing online. However, there are some differences that ultimately set them apart.
In this VPN vs forward proxy rundown, you will learn the differences between the two so you can decide which one will give you the best experience and protection.
Forward proxy and VPN – Overview
Before getting into details, here’s a quick summary of the key differences and similarities between forward proxies vs VPNs:
| Feature | Forward Proxy | VPN |
|---|---|---|
| ? Encryption | No | Yes |
| ?️ Location spoofing | Yes | Yes |
| ⚡ Speed | Fast | Fast |
| ? Cost | Most are free | Free and paid |
| ?️ Privacy of data | Weak | Strong |
Now, let’s break it down.
What is a forward proxy?
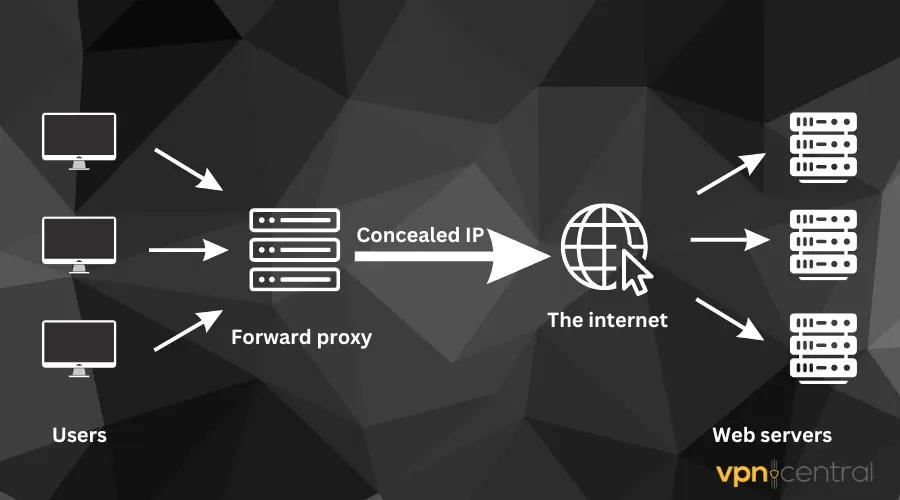
A forward proxy can be likened to a middleman that sits between the client’s device and the internet.
The forward proxy server evaluates a user request, hides the user’s original IP, and sends the request to the destination.
It then inspects and evaluates the response given by the web server and forwards it to the originating client as appropriate.
To put it simply, when you’re connected to a proxy server, you’ll access any website or app through an entirely different host server, not directly through your ISP.
This ultimately hides your identity and replaces your actual IP address with the proxy server’s IP address.
Asides from rerouting user traffic as appropriate, it protects users from having direct contact with snoopers, which may in turn compromise their data, making them susceptible to attacks.
What is a VPN?
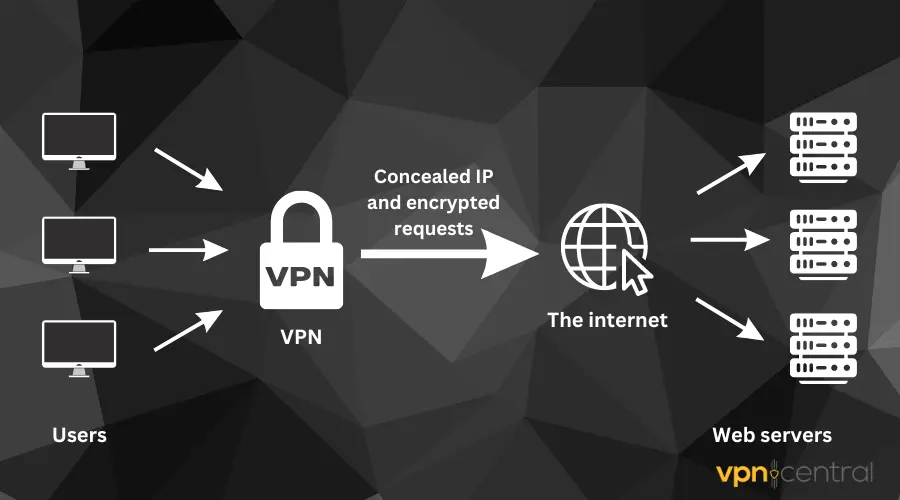
A Virtual Private Network is a privacy tool that helps to hide your identity and location by rerouting all your internet traffic via a remote server.
This makes it impossible for any website you visit once connected to a VPN to see your original IP, location, or internet activities.
It encrypts the traffic between your browsing device and the internet, such that your ISPs will be unable to track or monitor your internet data and activities.
Although they can see that you’re connected to the internet, everything you do remains hidden and unknown to them.
In short, it’s a tool that shields users from prying eyes, government surveillance, tracking, and hackers that may want to steal your data over a network connection.
They use military-grade encryption, which makes hacks almost impossible. Overall, a VPN provides users with heightened security features and internet privacy.
Now, let’s see how they compare in terms of features.
Forward proxy vs VPN
1. Encryption
A VPN encrypts all your data and internet traffic. This is the biggest flex a VPN has over the forward proxy server.
Once a VPN connection is established, any data you send or receive will be encrypted. This means that no one will be able to see what you’re up to online.
With that, you can rest assured while inputting your sensitive information like your credit card details on a website, knowing fully that cybercriminals won’t have access to your card details.
A proxy server on the other hand does not have device-wide encryption.
2. Speed
In theory, proxies should be faster because they don’t encrypt data before transmitting it.
However, since forward proxy connections are usually free, they tend to get overcrowded because people love free things.
This in turn takes a toll on connection speed as it slows it down and makes it less stable.
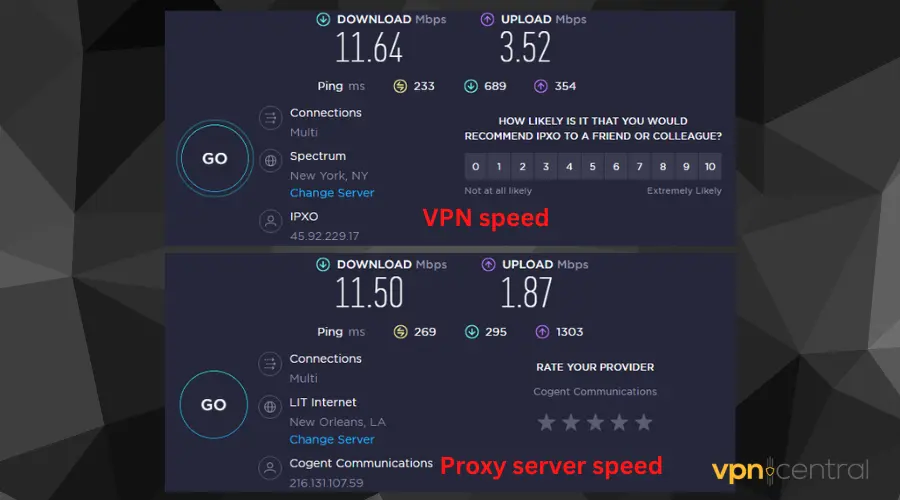
Consequently, according to our experience, a forward proxy server is slower than a VPN server.
Most premium VPN providers have employed certain techniques that make connections over the server fast without any hassle.
Below is the result we got when we put both tools to a speed test. The VPN had better upload and download speeds overall.
3. Anonymity
A VPN with strong encryption assures users of optimum privacy, especially when you choose a provider that operates a no-logs policy.
This ensures that the VPN provider does not store or track any information about you, as well as your internet activity once connected to their network.
Since they don’t store your information, they have nothing to turn over to the government or anyone that needs information about you or your online activities.
A forward proxy server on the other hand, since it’s free, is likely to monitor your internet activities, track and log your data and then sell it to third parties.
Those third parties aren’t generally malicious, they’re mostly advertisers. However, your data can become exposed if the proxy server or their third-party partners become the victims of a data breach.
As for no-log VPNs, there’s no data to steal, to begin with.
4. Cost
Some VPN providers are free while some are paid. Generally, those worth using are premium tier.
That’s because many free VPNs have a daily bandwidth limit to ensure that they evenly split their resources between their users.
Additionally, they may still log and sell your data so as to make money.
Therefore, for total online privacy, it makes sense to invest in a paid VPN. The good news is that reputable VPN services often offer good deals, starting from a little over 2$ a month.
Meanwhile, the majority of forward proxy servers are free. But there are paid options as well with the promise of a wider range of servers to choose from.
5. Reliability
A VPN connection is trustworthy and more reliable.
Reliable VPN providers have an in-built kill switch ( a security feature that helps prevent information or data leaks in case of a drop in internet connection).
In contrast, a proxy server connection is less reliable as it drops more frequently and puts users at risk of data leaks, as they don’t have any security features to prevent them.
When to use a forward proxy vs a VPN
Unable to decide when to use a VPN or a forward proxy? We’re here to help you.
When to use a forward proxy
Below are some situations when using a forward proxy can be really helpful:
1. Anonymize data requests
Requests sent over a proxy server use the IP address that belongs to the forward proxy instead of the user’s real IP address.
2. Bypass paywalls
Users can rotate their proxy server configuration to a different IP address to bypass paywalls on websites that offer limited free access.
Note that VPNs work for this as well, but the encryption and other additional features they have over proxies aren’t a must here.
3. Access region-locked websites
Some websites restrict access to visitors based on their geographical locations., especially those websites that use IP-based geolocation.
In this case, one can easily change their IP address with a forward proxy server to evade region locks and use restricted websites.
Note that some geo-locked sites have strict anti-proxy policies and do their best to detect and block them. However, they’re still a good and cost-effective option for accessing websites with less rigorous geo-locks.
4. Data protection
Using a forward proxy can help to prevent the spread of infected files in an organization.
Since a forward proxy inspects and evaluates every request, it can prevent users from uploading potentially harmful or sensitive information to cloud destinations.
When to use a VPN
Now, let’s see the best uses of a VPN:
1. Privacy from your ISP
Many ISPs monitor the data you send and receive over their network.
Using a VPN ensures that all your traffic is sent through an encrypted tunnel. This leaves your ISP with no information about you or your online activities.
Not only it maintains privacy, but it can also help bypass ISP website blocks and stop throttling.
2. Complete anonymity
A VPN ensures that you get adequate privacy from websites, search engines, and others who may track or monitor your IP address.
This means that it will be very difficult to trace back your location or determine your real identity.
3. Access to any content in any location
VPNs with strong unblocking abilities and wide server networks across the globe are able to bypass geo-restrictions and grant access to users from any location in the world.
4. Evade government censorship and bans
Is your favorite game or website banned in your country? No problem.
You can use a VPN to spoof your location and play banned games or visit banned websites without risking punishment or detection from the authorities.
5. Security and encryption
VPNs have a wide range of security features like AES 256-bit encryption, kill switch, and Split tunneling to help you beef up your online security.
They also use numerous tunneling protocols like WireGuard, OpenVPN, IPSec, IKEv2, and others just to ensure user identity is duly protected.
6. Secure browsing with public Wi-Fi
Connecting to public WiFi leaves you at risk of malicious attacks and hacking. This is because they are usually not protected with a password or they use weaker ones.
Using a VPN on your browsing device reduces this threat as all your traffic is encrypted and tunneled through secure servers.
Conclusion
Forward proxies and VPNs serve as a screen between a user’s device and the server they are interacting with. This makes it easy to evade censorship and spoof locations.
However, A VPN is a safer and more secure option due to its encryption feature that protects all data transmitted between the user’s device and the server
On top of that, the VPN allows coverage for all internet traffic while a forward proxy allows coverage for one app or website at a time.
VPNs hide the user’s IP address and encrypt all the data. Forward proxies, on the other hand, hide the user’s IP address but don’t encrypt any data.
Therefore, in a VPN vs forward proxy battle, it’s clear that a VPN is the better option if you want complete privacy, but proxies are pretty good at bypassing certain web restrictions and are the cheaper option.









User forum
0 messages