Is Your Router Blocking VPNs? Here’s How to Fix This [Updated 2025]
Your go-to guide for bypassing router blocks and accessing the web hassle-free.
11 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help VPNCentral sustain the editorial team Read more

Is your VPN blocked by the router? Don’t sweat it! It happens to a lot of us, and I’ll show you how to fix it, step-by-step.
A lot of ISPs configure their equipment to block VPNs. There are obvious reasons for doing so, such as security concerns and regulatory compliance.

Access content across the globe at the highest speed rate.
70% of our readers choose Private Internet Access
70% of our readers choose ExpressVPN

Browse the web from multiple devices with industry-standard security protocols.

Faster dedicated servers for specific actions (currently at summer discounts)
However, for you, this means you can’t disguise your IP or encrypt data – which is what makes the VPN in today’s state of the internet — an irreplaceable user resource. Not to mention you won’t be able to access any region-locked sites.
But as I said, there is a solution, so if you’re ready to stop your router from blocking your VPN service/routers blocking Ethernet VPN, keep reading.
How to unblock VPN when blocked by the router (ISP)?
1. Change the IP address
A certain server/IP location may be blocked, in which case switching to another server can help. You can easily do this from your VPN’s app, or switch the OpenVPN configuration if you installed the VPN directly on your router.
Here’s what you need to know:
➡️Change IP address in the router setup panel
Head to your router’s control panel and configure a new VPN connection with another OpenVPN server.
A good VPN to configure on your router, with OpenVPN support for all its locations is ExpressVPN. Here’s how to configure it:
- Get an ExpressVPN subscription plan.
- In a browser, access your ExpressVPN account.
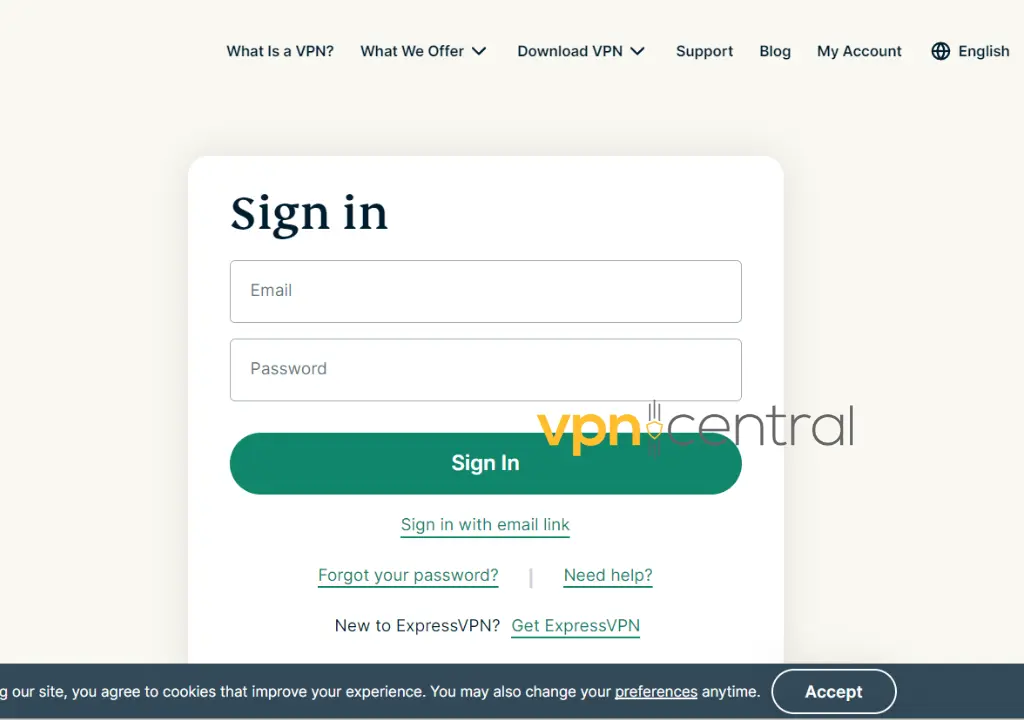
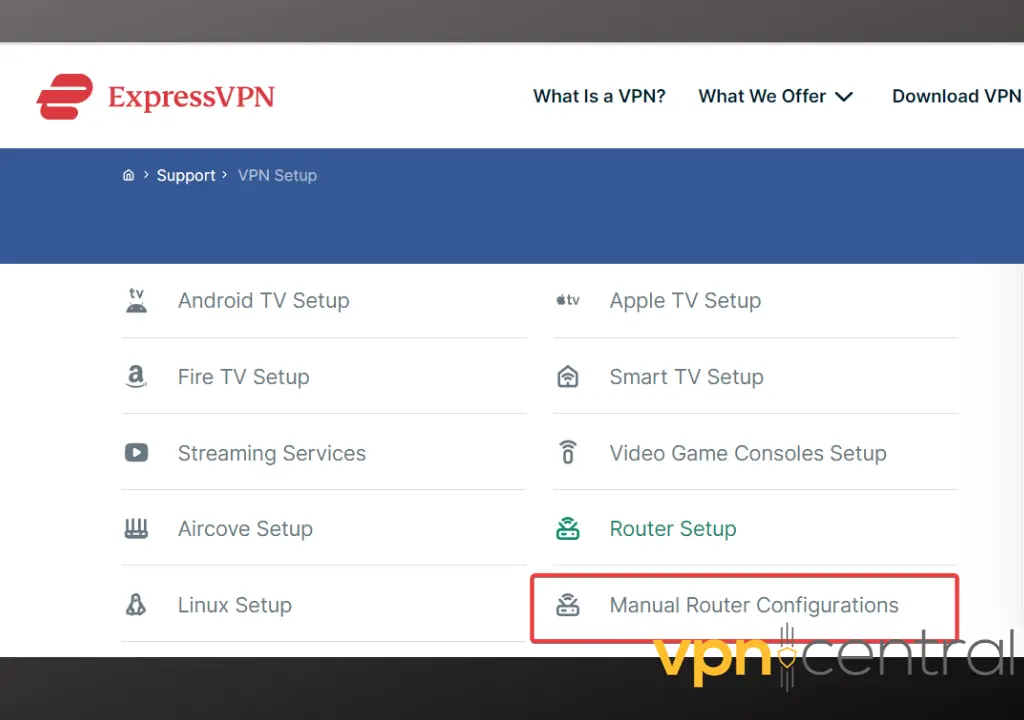
- Head to the setup page.
- Pick Manual Router Configurations.
- Select your router or firmware model and download the OpenVPN configuration files for the server you want to connect to. Pick a different location from the one you’re currently using.
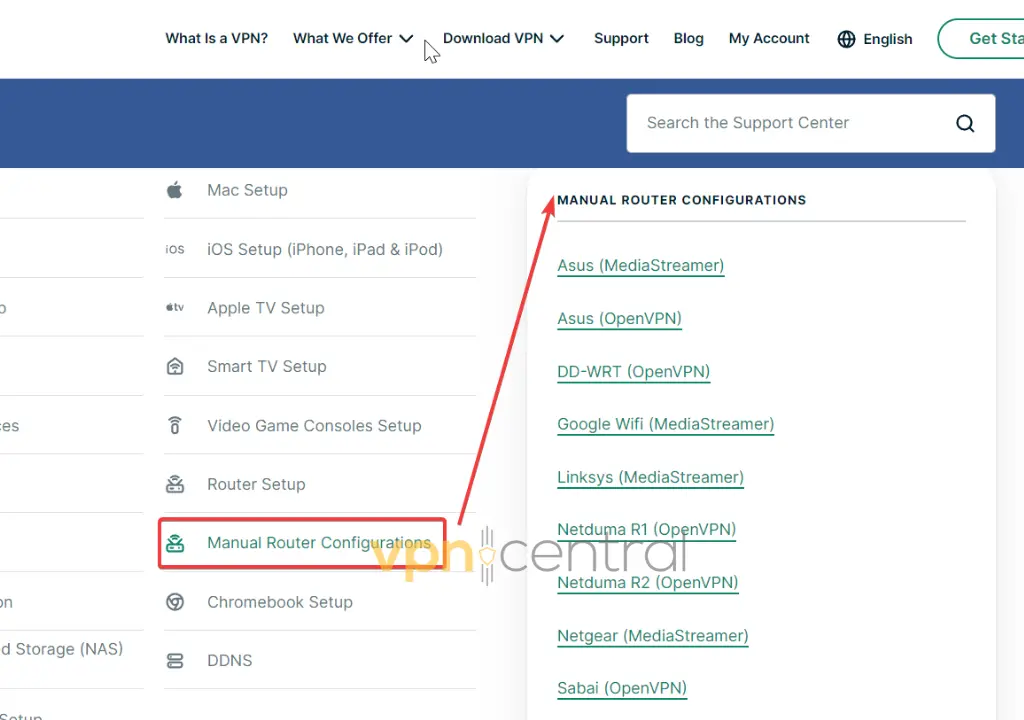
- Head to your router’s setup panel and create a new VPN network profile.
You can also install ExpresVPN natively, on all devices on your network. It offers dedicated apps for PC, Android, iOS, macOS, and more.
Here’s how to change your IP directly from the software:
➡️ Change IP address in the VPN app
- Open your VPN application.
- From the main menu, click on the server list. In general, it appears next to your current location, tagged as “Servers”/”All Servers” or “Server List”.
- Browse through the list of servers and select another one.
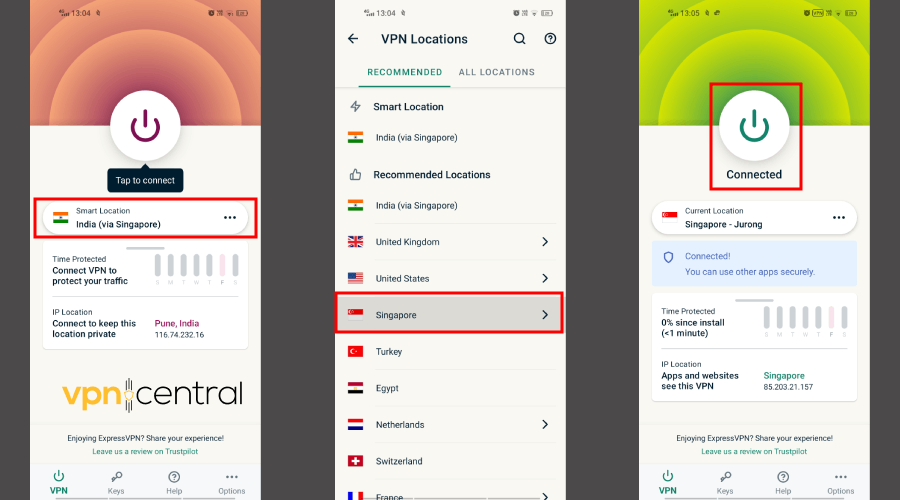
- Once connected, open a web browser and check if you have internet access.
If you don’t have a compatible router, you can still install a VPN if you flash your router. Check our guide on how to set up a VPN on Huawei routers for more in-depth information.
Our recommendation goes to ExpressVPN because it’s a world-leading VPN with a massive network composed of 5,000+ servers in over 100 countries.
ExpressVPN is good at helping you get around restrictions, whether it’s from your internet provider, your country, or other rules. And it keeps your data super safe with strong encryption too.

ExpressVPN
Don’t lose any sleep over your router blocking your VPN. Team up with ExpressVPN and enjoy ISP throttling-free web action!2. Change the protocol
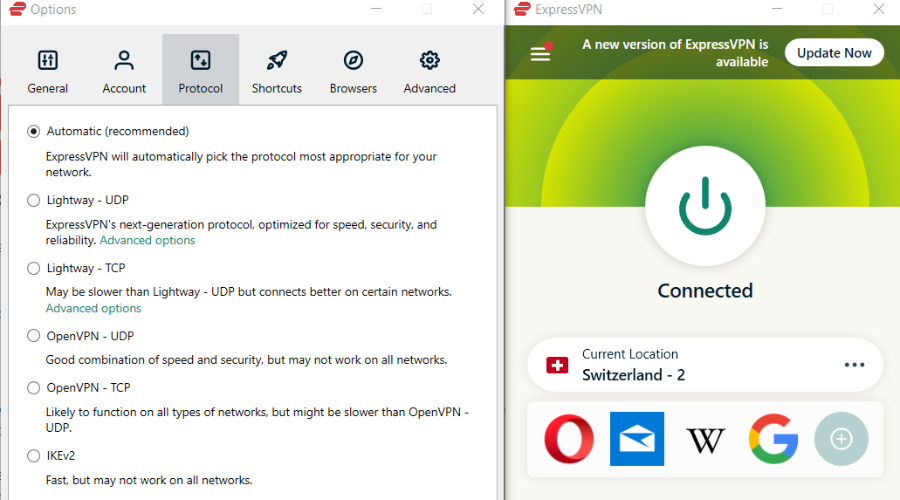
Lots of routers block standard VPN protocols, like Point-to-Point Tunneling (PPTP) or SSTP.
There’s probably an option that allows you to allow these protocols to communicate freely, but it’s easier to manipulate settings within the VPN tool itself.
What you can do is switch between the available protocols until you find the one that will likely work. Our best bet is to stick with the OpenVPN.
In addition, it hardly gets any blockage by default from the ISPs, which is, in this case, the most important trait.
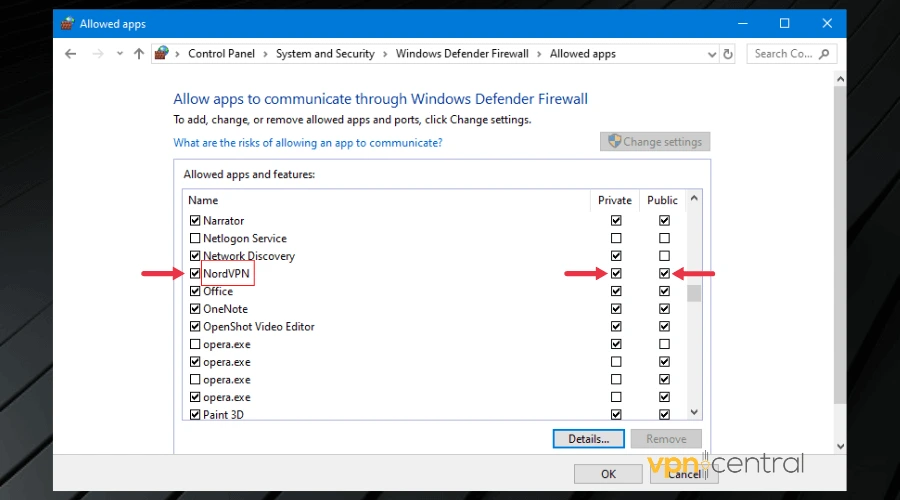
3. Allow the VPN through the firewall
Adjusting firewall settings to allow your VPN can resolve connection issues caused by the firewall blocking the VPN’s traffic.
➡️ For Routers:
- Access your router’s admin panel, typically through a web browser.
- Navigate to the Firewall or Security settings.
- Look for an option to create rules or exceptions.
- Add a rule to allow traffic from your VPN, using its application name or the ports it uses.
- Save your changes and restart the router if necessary.
➡️ For PCs (Windows):
- Open Control Panel and select System and Security.
- Click on Windows Defender Firewall and select Allow an app through the firewall.
- Find your VPN app in the list, check both Private and Public boxes, or click Allow another app to add it.
- Save your changes.
➡️ For Macs:
- Go to System Preferences and select Security & Privacy.
- Click the Firewall tab and then Firewall Options.
- Click the + button to add an application, and select your VPN app.
- Ensure it’s set to Allow incoming connections.
- Click OK to save your changes.
This method helps when your network might wrongly flag or block your VPN for security reasons. This happens regularly, regardess of device, so it’s worth trying.
A word of warning – always add your VPN as an exception to the rule and never disable your firewal/antivirus. It’s not worth exposing your device to cyber attacks.
4. Enable port forwarding for your VPN
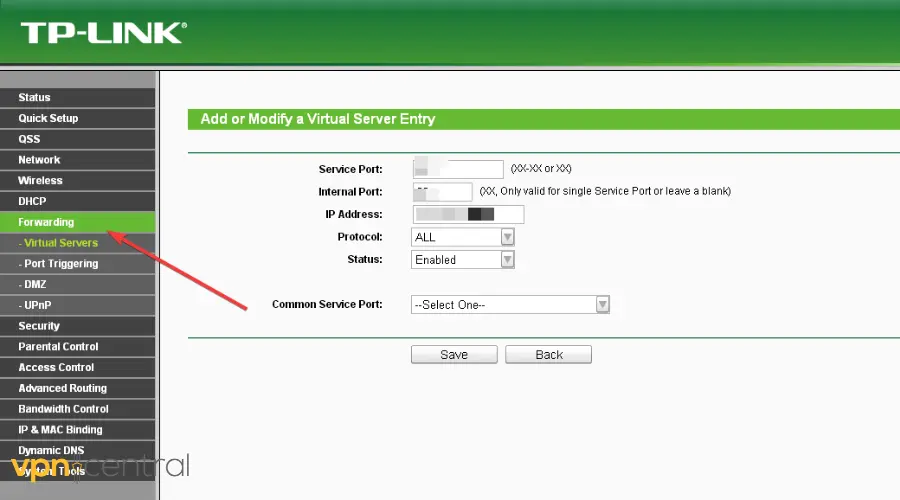
Port forwarding can help when your router doesn’t naturally allow VPN connections. It directs the VPN traffic directly to your device by specifying port numbers.
How to do it varies depending on the router model, but here’s the basic process:
- Log into your router’s admin panel. Usually, you have to type an address like
192.168.1.1or192.168.0.1in your web browser. The specific address should come with your router’s manual. - Find the “Advanced Settings” or “Port Forwarding” section.
- Enter the port numbers used by your VPN. They’re different for each provider, so you’ll have to look in your settings, user dashboard or your VPN’s FAQ pages.
- Specify the IP address of the device you’re using the VPN on.
- Choose TCP/UDP as the protocol, if asked.
- Save your settings and restart both your router and your device.
5. Enable VPN pass-through
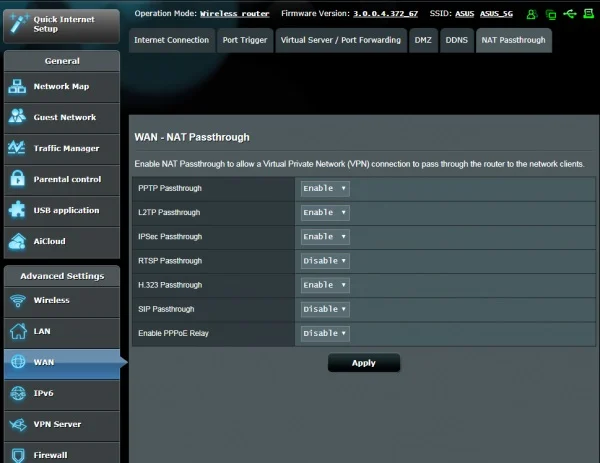
VPN pass-through enables support for VPN protocols that your router might block by default.
Here’s how to do it:
- Access your router’s settings interface through your web browser. You usually have to enter an address like 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1. The exact address should come with your router’s manual.
- Look for the “VPN,” “Security,” or “Advanced Settings” menu.
- Find options labeled “VPN Pass-Through” or something similar.
- You will most likely find separate options for different protocols such as OpenVPN, PPTP, L2TP, and IPSec.
- Enable these options for all the protocols.
- Apply or save your changes, then restart your router.
This setting is crucial if your network blocks VPN connections or if you’re having trouble establishing a VPN connection.
It’s making sure your router’s firmware supports these protocols and doesn’t automatically block them.
6. Use VPN Obfuscation
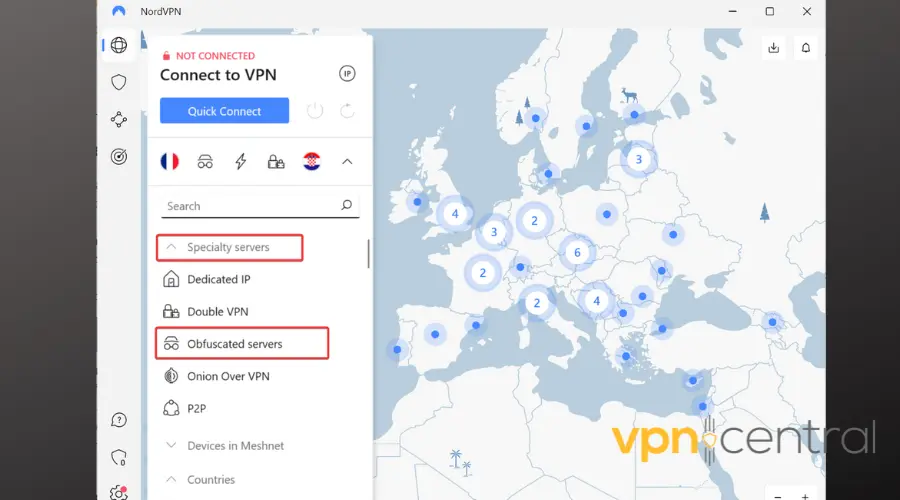
VPN obfuscation disguises your VPN traffic. It’s an advanced feature that can prevent VPN blocking by router.
Here’s how to do it:
- Open your VPN application on your device.
- Look for “Settings” or “Preferences.”
- Find an option labeled “Obfuscated Servers,” “Stealth Mode,” or similar.
- Enable this feature.
- Reconnect to your VPN, choosing an obfuscated server if available.
This option disguises your VPN traffic as regular HTTPS traffic, making it harder for routers and firewalls to detect and block the VPN connection.
7. Try using Ethernet
A temporary solution you can try if your WiFi is blocking VPN is switching to an Ethernet connection. It provides a direct line to the internet, potentially avoiding these blocks.
- Find an Ethernet cable that is long enough to reach from your router to your device.
- Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to an available port on your router.
- Plug the other end of the Ethernet cable into your device’s Ethernet port.
- Turn off Wi-Fi on your device to ensure it uses the Ethernet connection.
- Retry connecting to your VPN to see if the issue is resolved.
This method bypasses wireless-specific restrictions.
How do I know if my ISP is blocking my VPN?
The biggest giveaway is that you can establish an Internet connection, but once you try to connect to your VPN, you are suddenly offline.
? If your VPN doesn’t work on any device on your local network, but the connection is up otherwise, then it’s very likely that the router is blocking the VPN.
Luckily, there are ways to make your VPN connection untraceable so your ISP won’t know what to block in the first place.
How to block VPN on a router?
If you’re curious about how routers are able to block VPNs in the first place, you might be surprised. There isn’t one straight way to do it, but several:
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI): Routers check data packets and might stop VPN traffic if they spot it.
- Port Blocking: Routers can stop certain ports that VPNs use, like TCP 1723 for PPTP or UDP 500 for L2TP/IPsec.
- VPN Protocol Restrictions: Some routers only allow certain types of VPN connections by default.
- Firewall Rules: Routers have built-in firewalls that can block VPN traffic based on specific details.
- DNS Filtering: Routers might prevent access to VPN websites or stop DNS requests related to VPNs.
- VPN Passthrough Issues: If VPN passthrough isn’t enabled, the router might have trouble with VPN traffic.
- ISP-Level Blocking: Internet providers sometimes block VPN traffic as part of their network management.
- Firmware Limitations: Older router software might not work well with modern VPNs, causing problems or blocks.
And if your router/ISP really wants to block VPN, it will likely use more than one method to make sure nothing passes through.
Why is my router blocking the VPN?
Here are a few things to consider when facing this issue:
- Your router and VPN are not compatible
- The VPN protocol of your client isn’t supported by the router
- If you use two routers, make sure your main router allows VPN passthrough
- Security – check your router’s settings and make sure you allow VPN through the router firewall
These are just a few quick things you can try. Moving on, we will show you more in-depth fixes with step-by-step explanations so you can use VPN on your router in no time.
Which router can block VPNs?
While there isn’t a complete list, some common routers that restrict or have had problems with VPNs include:
For more specific information, we recommend contacting either your VPN or ISP tech support, as they’re responsible for the execution of the application.
How do I know if my router supports VPN?
First off, you must know in which of the 3 main categories router falls into.
- ISP-provided routers as the name implies are owned and managed by your ISP. They have restrictions and usually don’t allow the use of VPNs.
- Off-the-shelf (OTS) routers are easier to work with as they have no ISP-enabled restrictions but not all of these support VPN. Check for OpenVPN Client compatibility.
- Custom firmware routers – usually come with tons of features that allow for modifications and customization based on user preference. They are mostly for tech-savvy people as it’s usually not an easy task setting up a VPN on this type of router. The majority of ZTE and Netgear routers are good examples.
Now, to find out if your router supports the use of a VPN, you need to do a few things.
- Check the manufacturer’s website or the configuration interface to be sure that the router supports acting as a VPN client.
- Ensure that both your router and VPN provider support the same protocols. Most routers work with OpenVPN.
If you’ve done both checks and you find that your router doesn’t support a VPN natively you’ve got one last option – to install third-party firmware.
OpenWrt, DD-WRT, and Tomato are examples of third-party firmware you can install on your router.
Changing your firmware (also known as flashing your router) is a bit complicated because you essentially have to switch to a different operating system.
Good news is, most third-party firmware options offer dedicated guides for it. And once you install it you can easily setup VPN on your router.
Use these links to check the lists of supported devices for OpenWrt, DD-WRT, and Tomato respectively. The good news is they are free.
However, they too have their pros and cons.
- OpenWrt supports lots of devices and has a good update system but it has a complicated setup process.
- DD-WRT is user-friendly and has a strong firewall. However, it doesn’t support lots of devices and has limited advanced features.
- Tomato doesn’t work on all routers and devices but it has the most user-friendly interface.
Conclusion
With that, we can conclude this article. In case you have a recommendation or question, feel free to post them in the comments section below.









User forum
4 messages